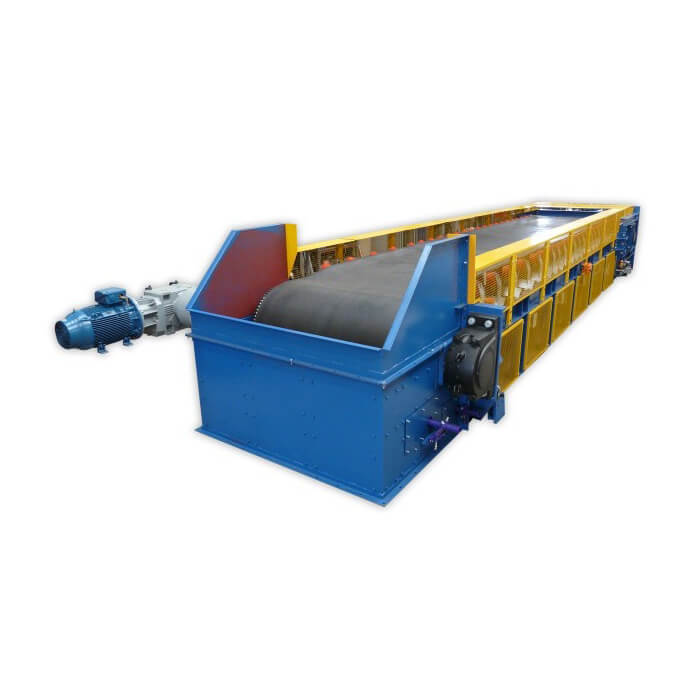
Belt Feeder
Capacity: 10-450 t/h
Power: 1.5-2.5 kW/Meter
Belt Width: 500-1000 mm
Applicable Materials: Suited for applications in gold, copper, coal, zinc, alumina, bauxite, iron ore, limestone, lignite, rock, phosphate rock, salt, sand, and more.
Belt Feeder Overview
The belt feeder is a device for continuous conveying, weighing, and feeding control of bulk materials. It can cooperate with the process requirements in the production process of various industrial enterprises to form an intelligent and automated production system. It is widely used in the chemical industry, building materials, cement, food, and other industries.
High-performance belt feeders are designed to move materials from hoppers and bins. They are the main feed unit for most crushing, screening, and cleaning circuits. Belt feeders are widely used in heavy-duty mineral processing operations.
Features
- When the belt feeder is used under a silo and hopper with a certain pressure, it can uniformly and continuously transport various large-capacity materials to various crushing, screening, and transportation equipment over a short distance.
- Compared with plate feeders, belt feeders are cheaper. Moreover, it is driven by the friction between the belt and the rotating parts such as the roller. The trough formation between the belt and the roller is very good, so there is a good seal between the guide groove and the belt so that the material is not easily scattered at the receiving area. The sealing performance can be selected according to the actual situation, or a baffle plate can be selected, both of which can prevent material from spreading, but sealing can prevent powdery materials from rising up and polluting the environment.
- Belt feeders are usually equipped with guide troughs throughout, which increases the transportation capacity of the feeder itself and improves transportation efficiency.
- Belt feeders usually have very low belt speeds and stable material transportation.
- Generally, a larger bandwidth is used because the belt speed is low. Increasing the bandwidth can improve the transmission capacity and save transportation costs.
- The design of the belt feeder roller set also has its own structural characteristics and layout. The supporting rollers of the belt feeder are generally composed of 4-5 roller sections. For large-bandwidth feeders, three rollers are usually used in the middle, and the total length is about 3/4 of the bandwidth. The side roller adopts a short roller and the groove angle is 20 degrees. This structure can not only increase the effective volume of materials but also adopt a three-point support structure in the middle, which increases the service life of the rollers and roller group beams.
- Since the material is transported throughout the whole process and the belt speed is low, the material on the feeder will increase the pressure on the side of the guide trough. In the design of the guide trough, try to use only one or both ends of the guide trough, and when using multiple sections of the guide trough, the connections should be staggered to prevent material from jumping. Moreover, the legs of the pouring chute also strengthen the structure to ensure the stability of the structure and system.
- Correcting devices are installed on both sides and front and rear of the feeder to effectively prevent the belt from wandering.
- Cleaners can be installed at the head and tail of the belt feeder, which is responsible for cleaning the materials remaining on the belt, avoiding repeated weighing of accumulated materials, and effectively protecting the life of the belt. In addition, the use of automatic cleaning devices reduces the maintenance of the belt feeder and reduces the workload.
Belt feeders are widely implemented in coal mining operations, where the material is composed of smaller lumps that are less than 20″ in size.
Advantages
Belt Feeder Advantages
- High-quality Belt Feeders designed with dependability in mind.
- Our Belt Feeders deliver a high-quality performance and long life.
- Robust Belt Feeders that operate with efficiency and ease.
- Safety features protect your operators.
- The dimensions and sizes of the belt feeders can be customized to suit your layout and material characteristics.
Structures & Working Principle
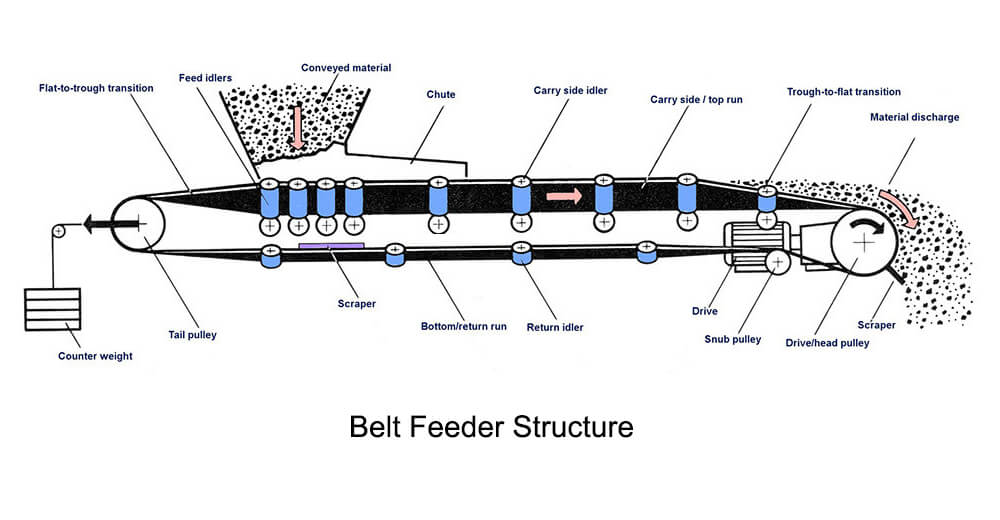
Belt Feeder Structures
The belt feeder consists of the belt, skirt board, impact idlers, drive system(drive/head pulley), tail pulley/takeup, feed hopper, discharge chute, control system, etc.,
Belt Feeder Working Principle
The belt feeder consists of a hopper positioned directly over a belt conveyor. The belt conveyor “pulls” material out from under the hopper. At the same time, an adjustable vertical strike-off plate controls the height of material allowed to advance as the belt moves forward, or in other words, the material profile on the belt. Skirt boards contain material on the belt.
Technical Parameters
| Model | Belt Width (mm) | Feeding Capacity (t/h) | Power Per Meter (kW) |
| 500×3000 | 500 | 10-100 | 1.5 kW/Meter |
| 500×4000 | 500 | 10-100 | 1.5 kW/Meter |
| 650×4000 | 650 | 10-100 | 2 kW/Meter |
| 800×4000 | 800 | 15-150 | 2.5 kW/Meter |
| 800×4500 | 800 | 15-150 | 2.5 kW/Meter |
| 1000×6000 | 1000 | 200-450 | 2.5 kW/Meter |














