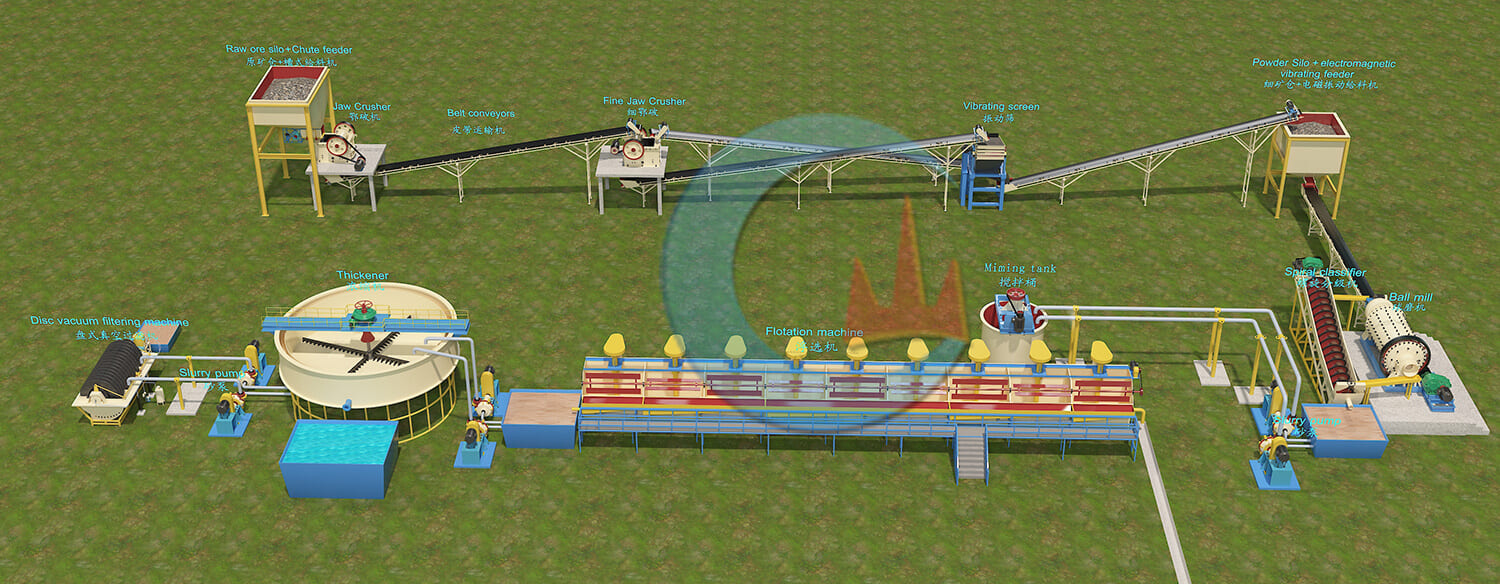
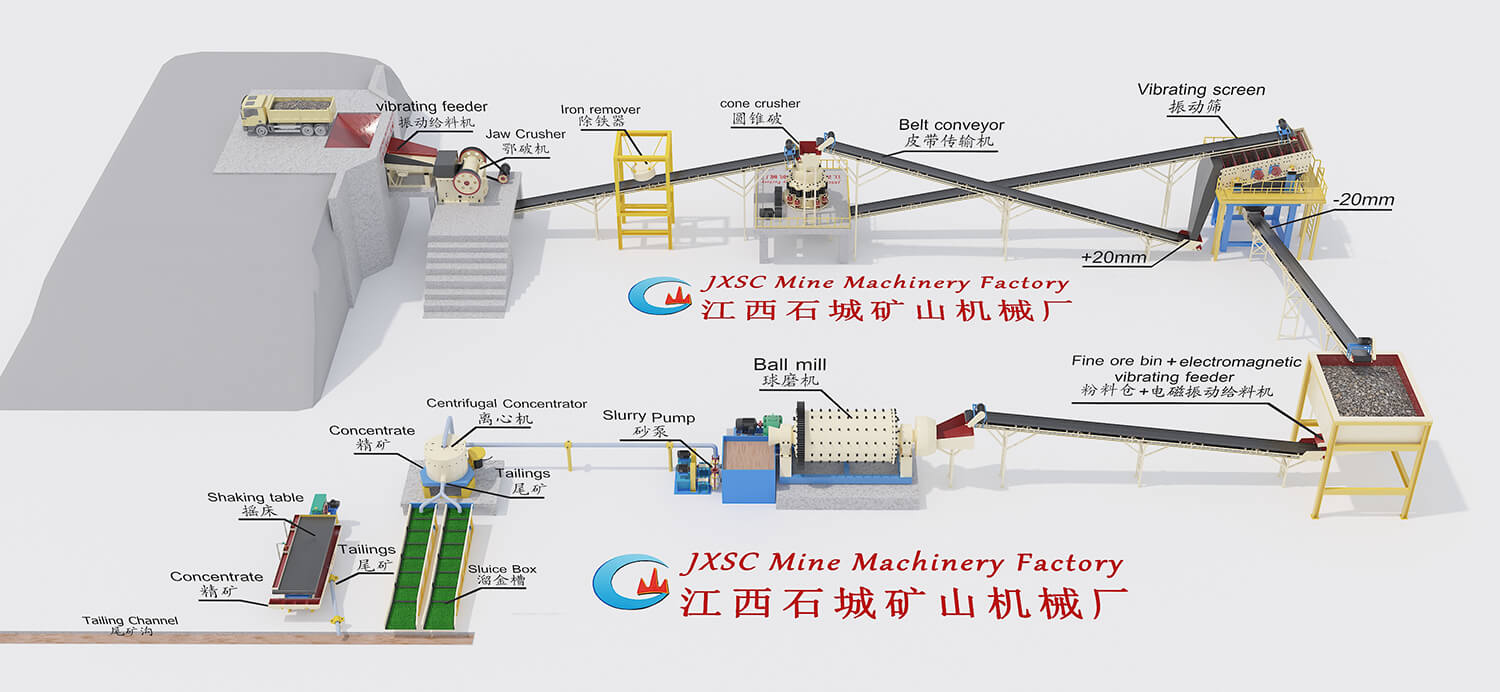
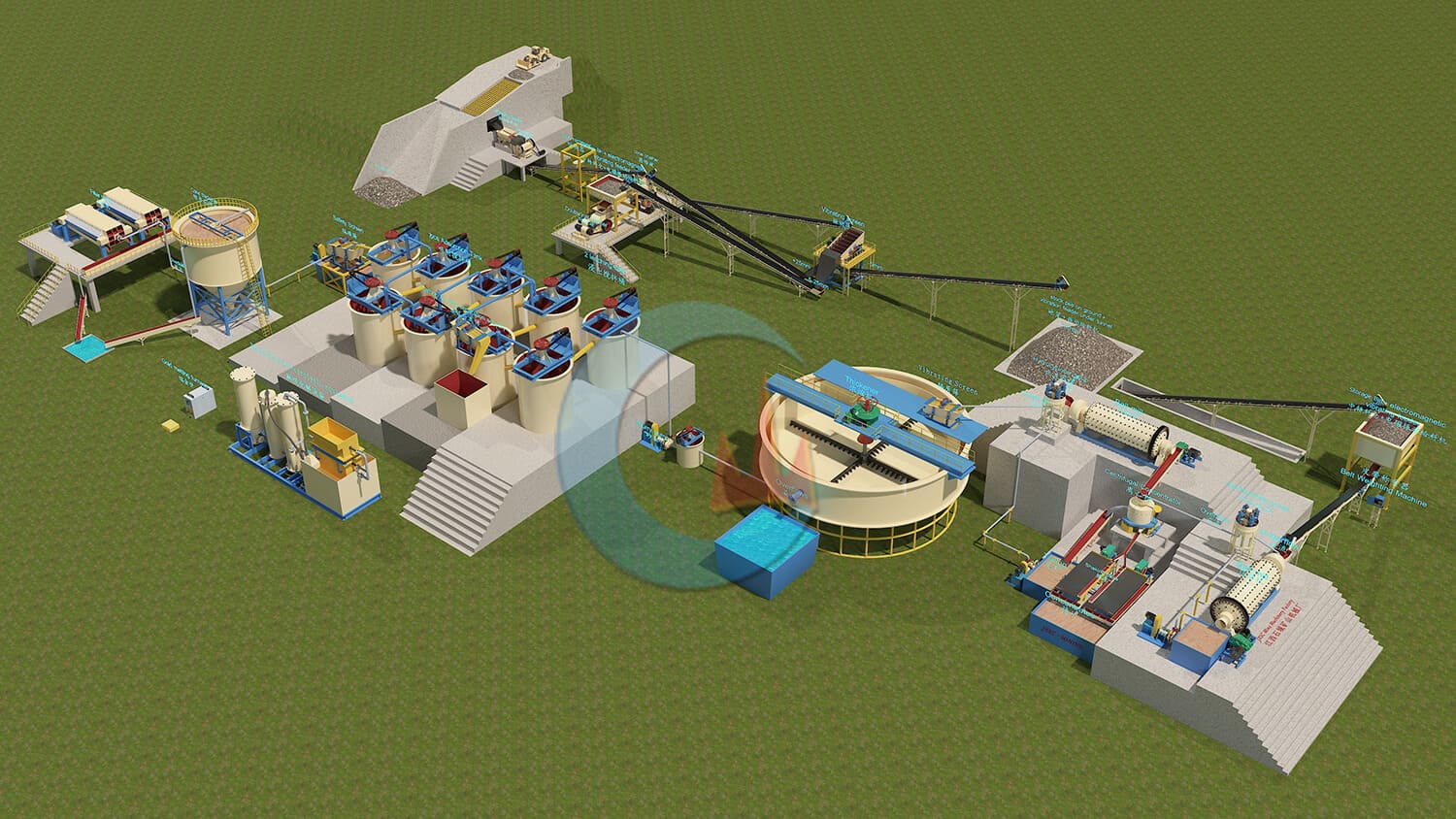
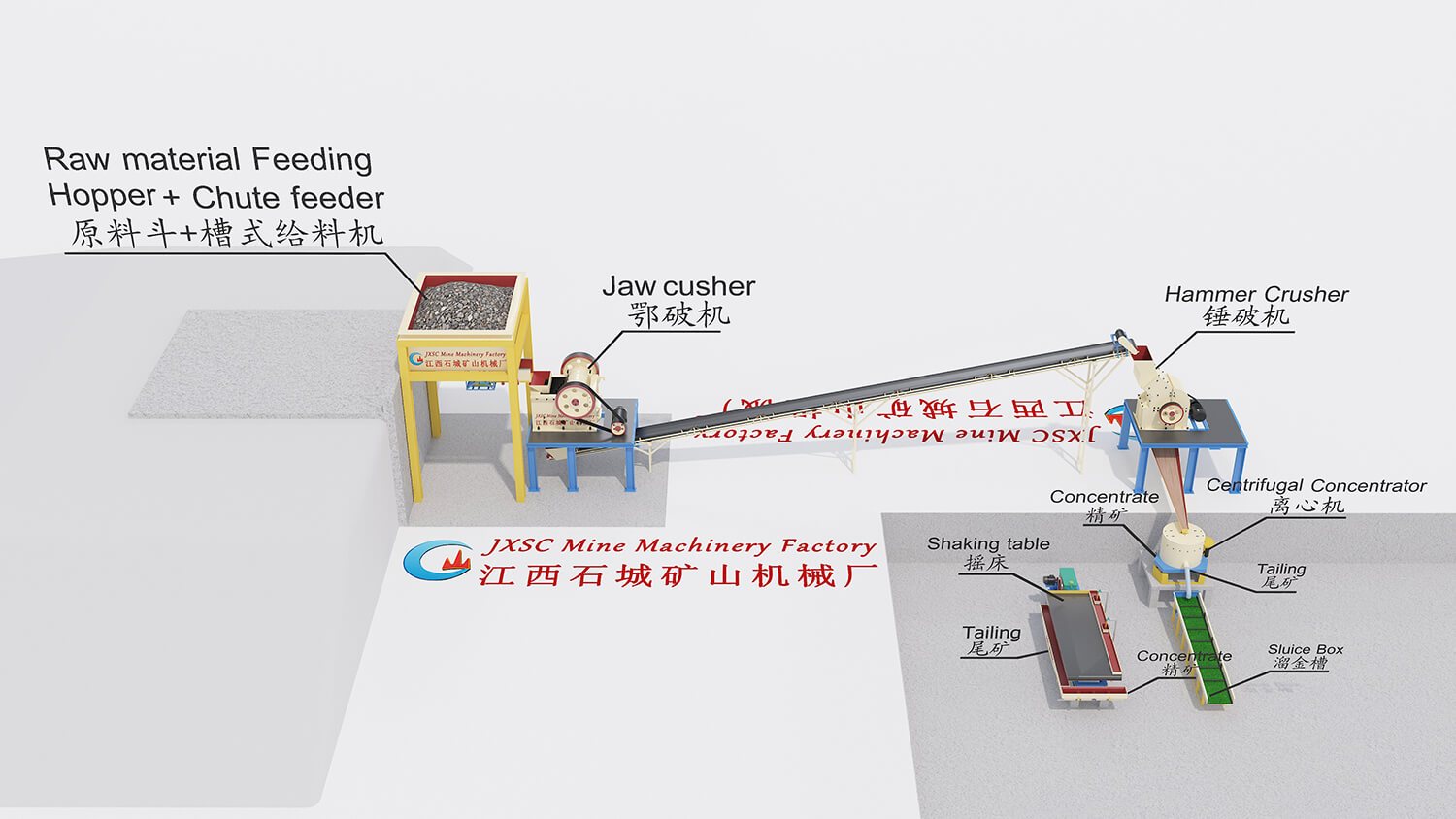
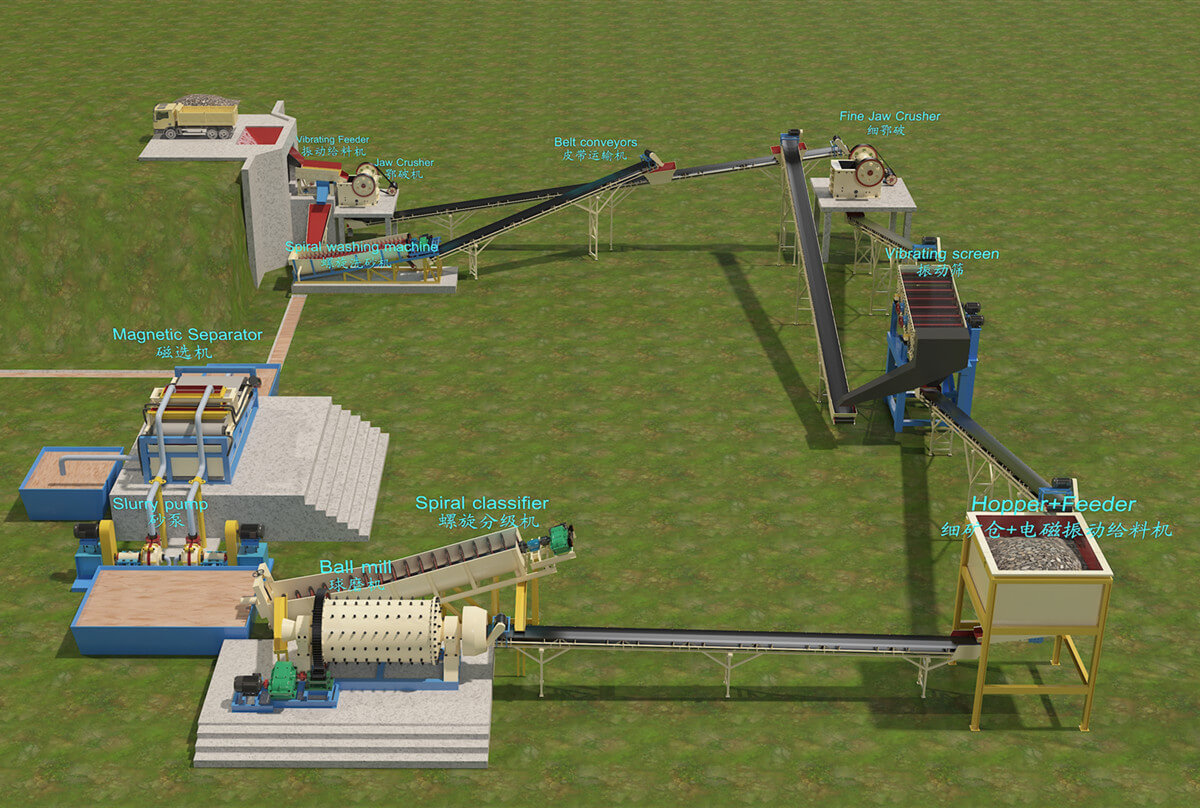
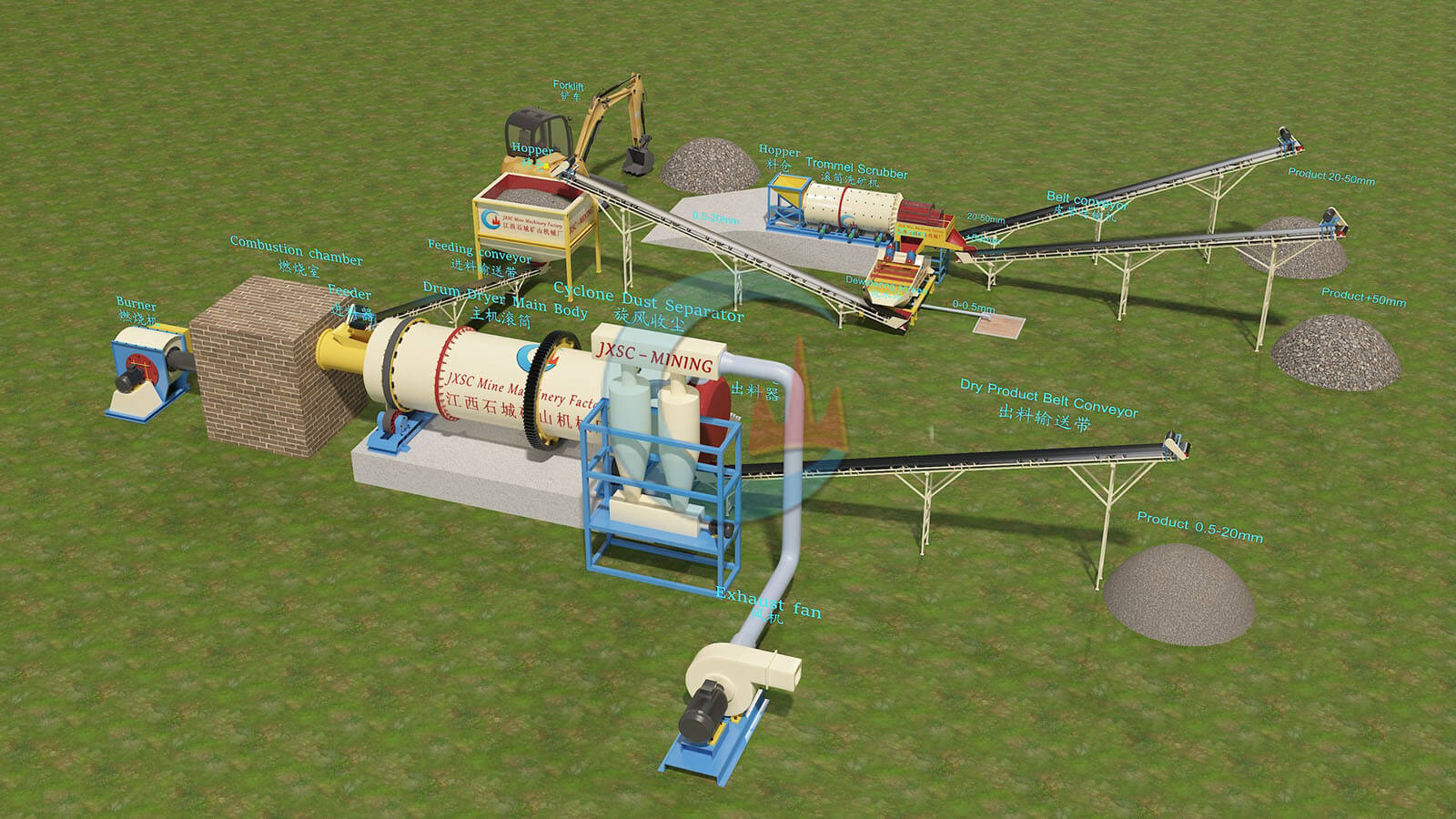
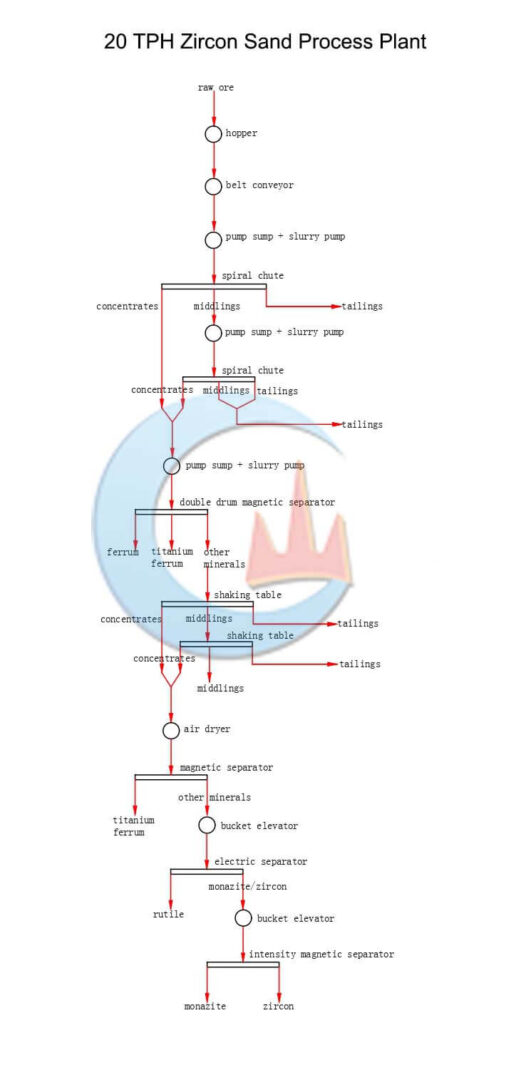
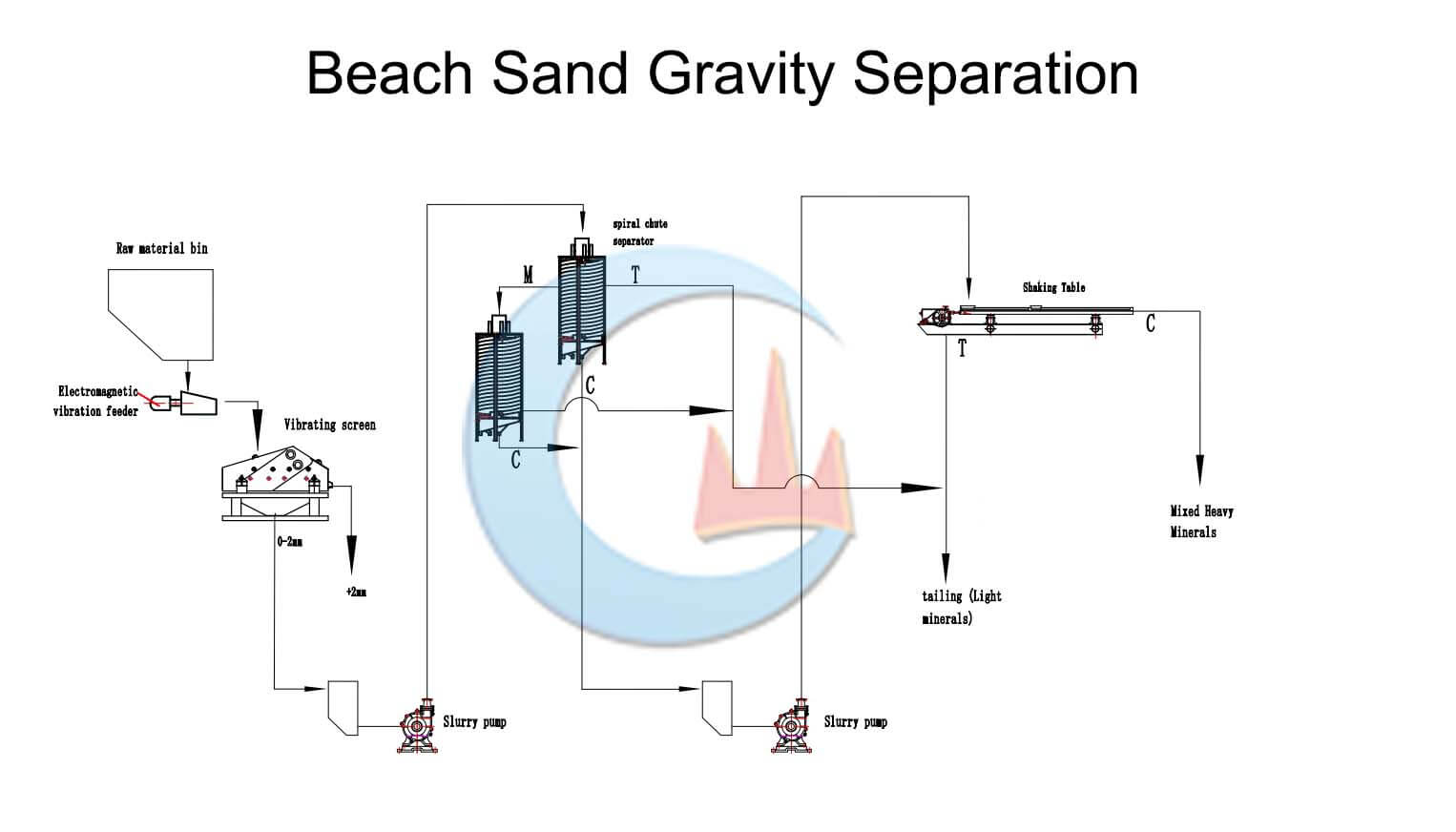
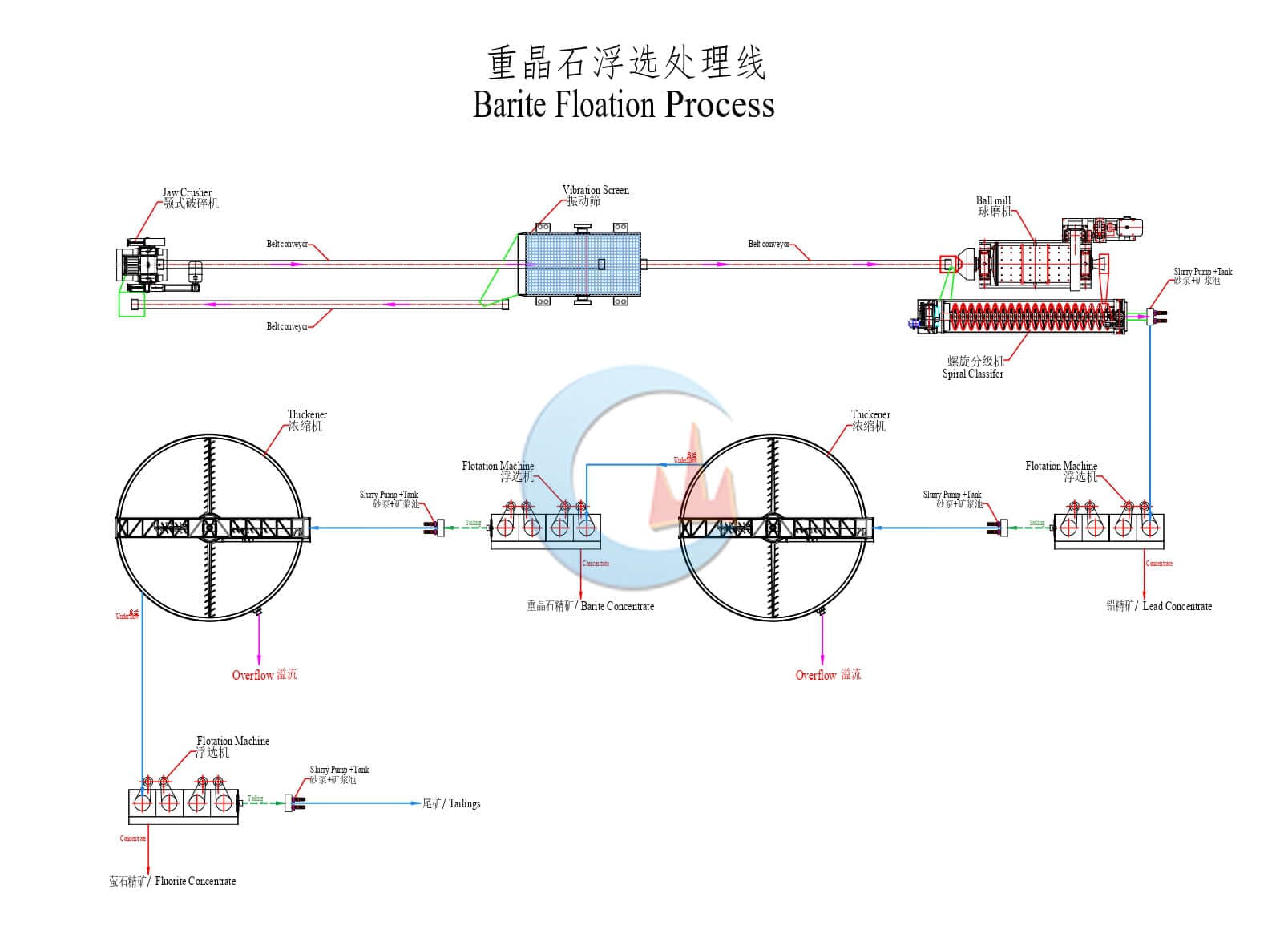
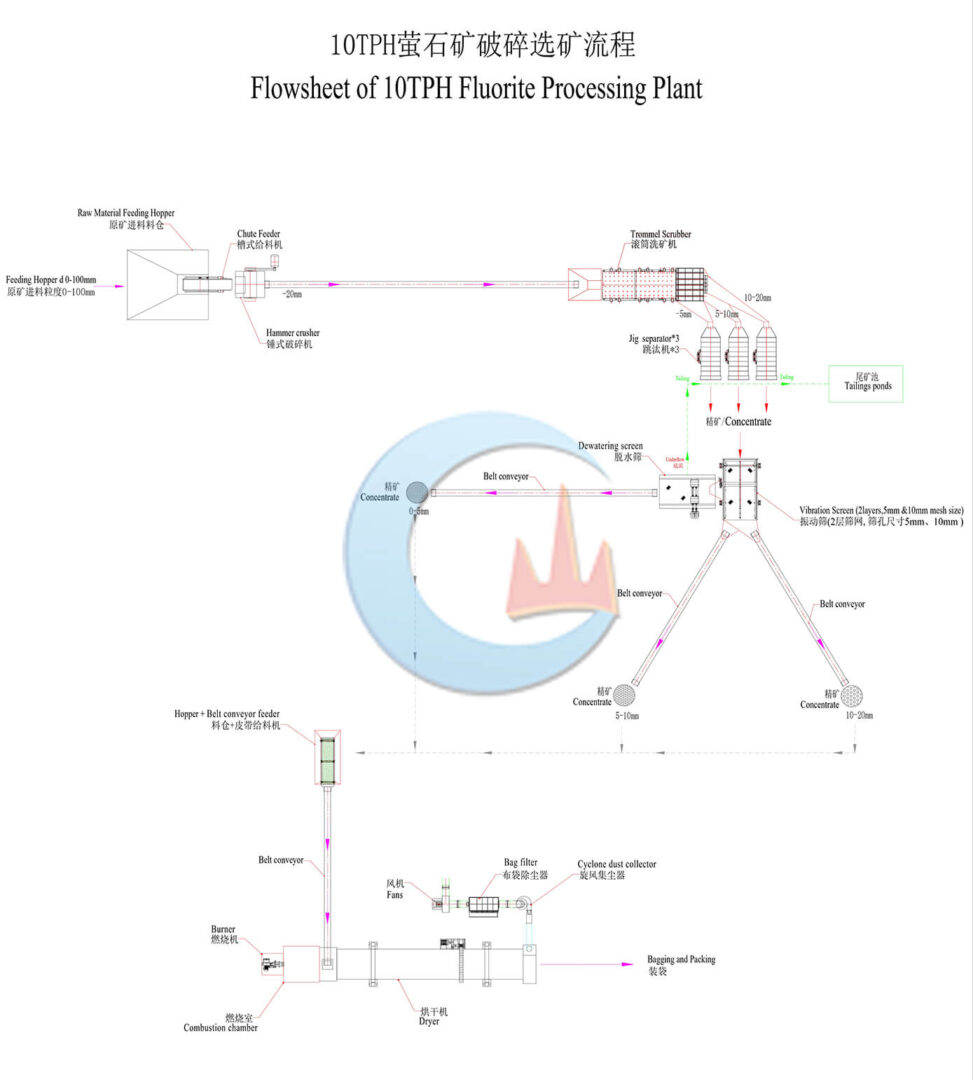
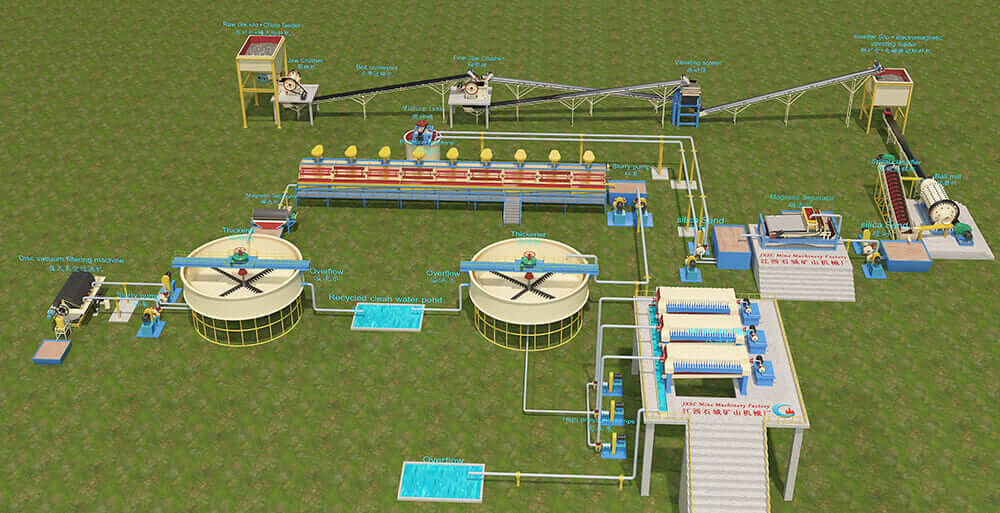
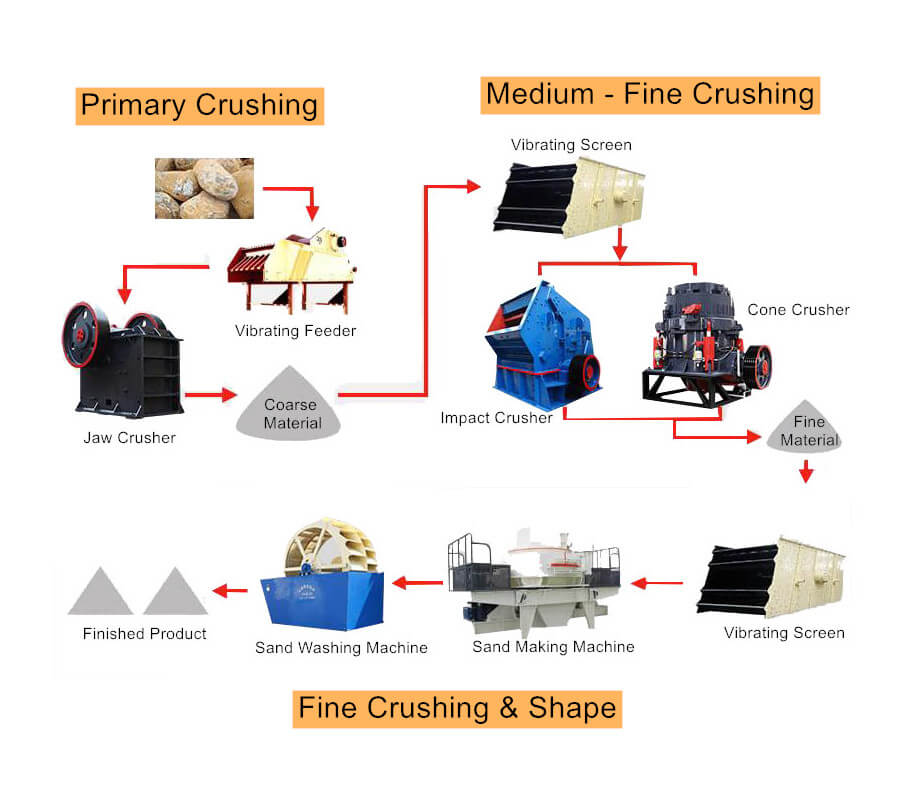
Mineral Mining Solutions
Mining Solutions
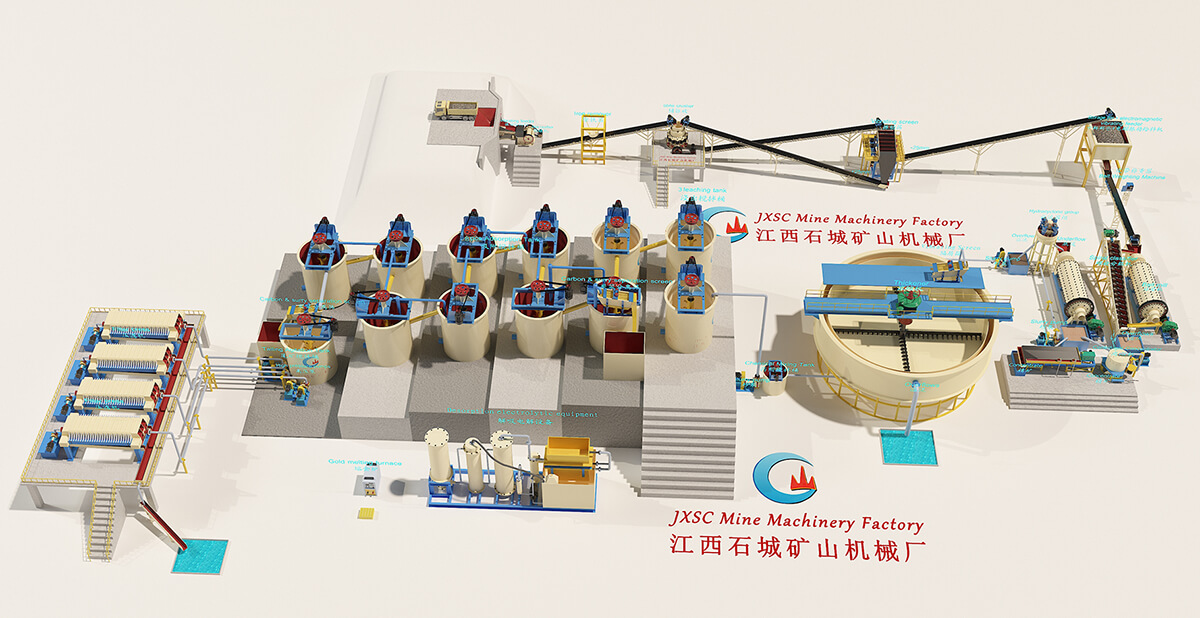
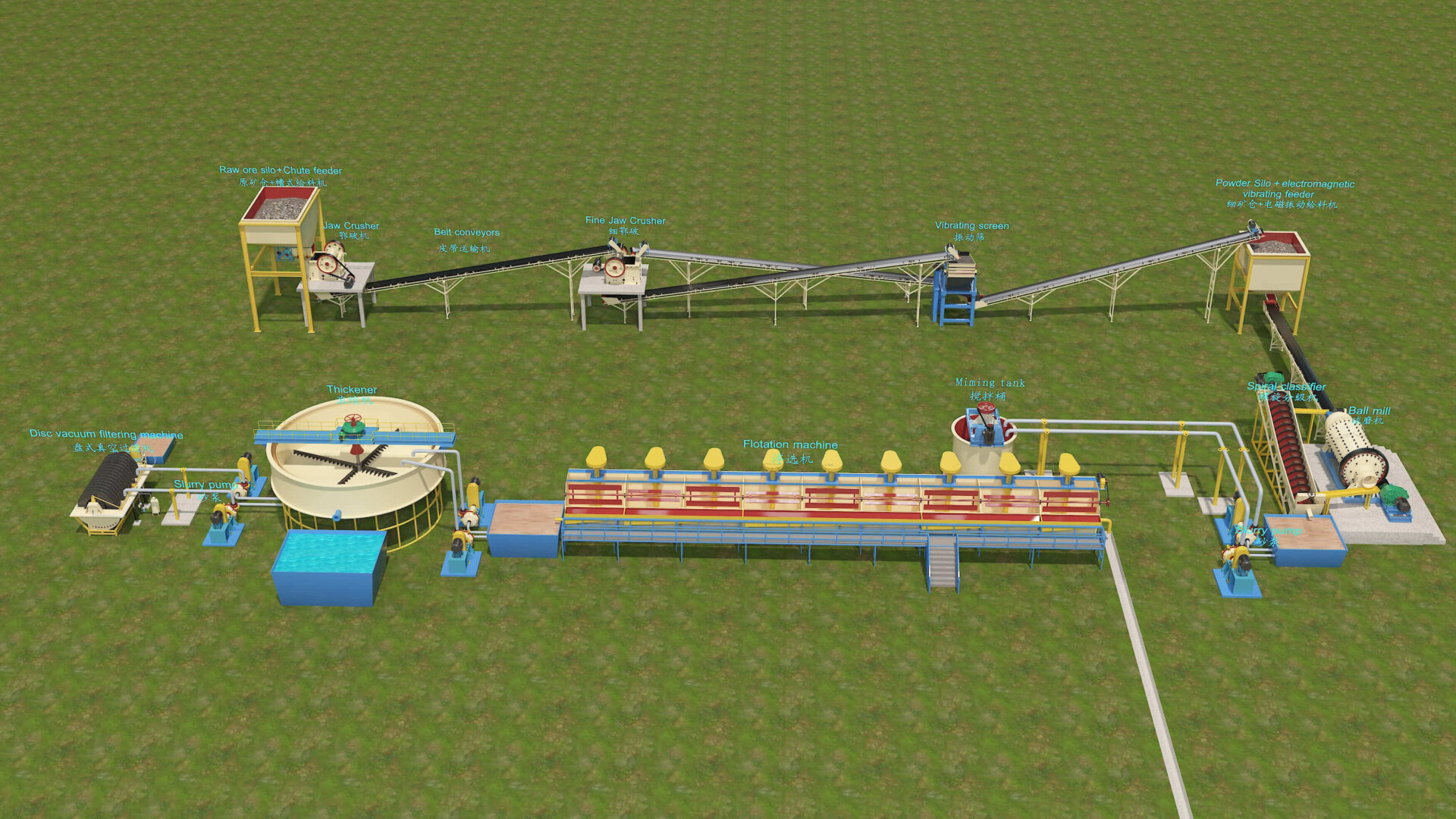
JXSC’s Mining Solutions business offers a series of metal, non-metal, and tailings solutions. We focus on the research of mining solutions, which increase productivity, recovery, and flexibility throughout the mining operations including leaching, solvent extraction, flotation, solid/liquid separation, and tailings management. Our diverse range of mineral processing technologies improves process efficiencies and aids the economic extraction of valuable resources.
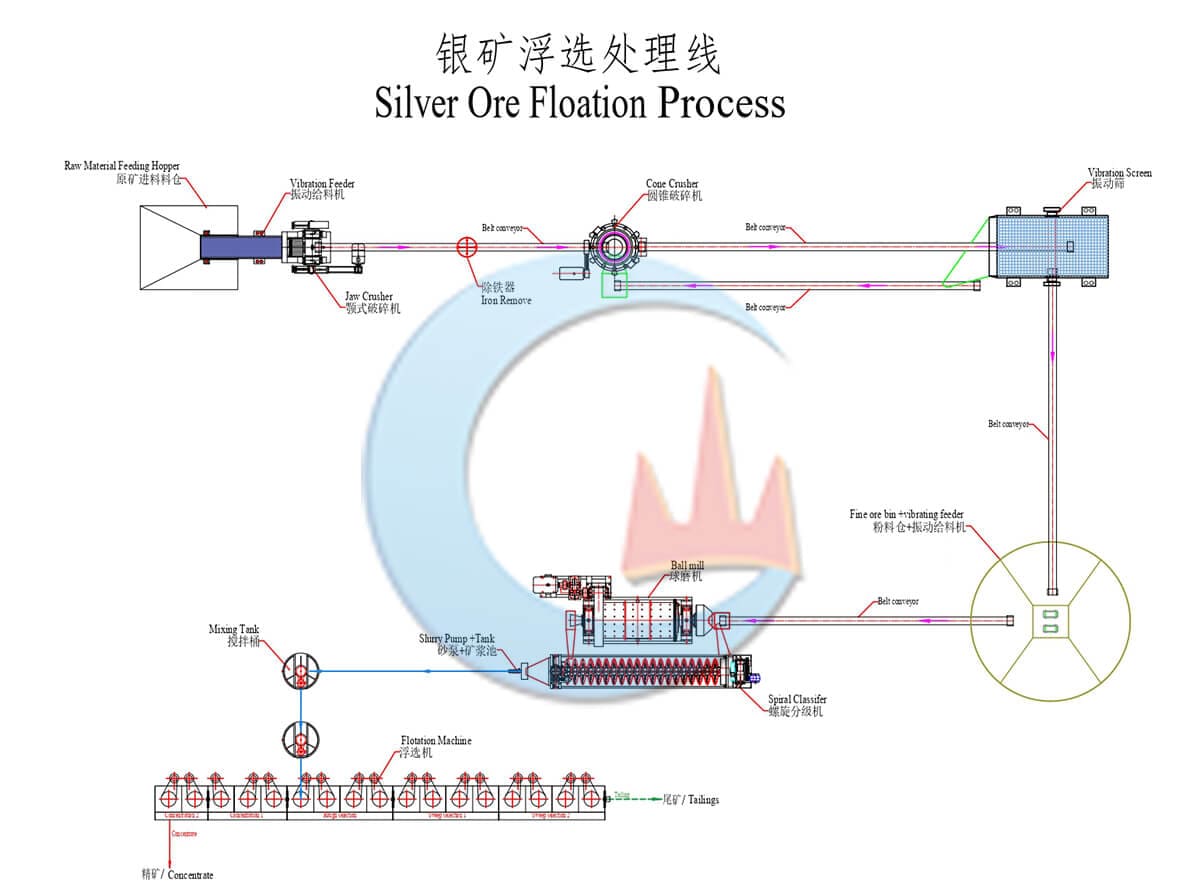
Precious Metal
Precious metals are naturally occurring metallic elements with high economic value due to their rarity, beauty, and various industrial and cultural uses. These metals are typically characterized by their luster, malleability, ductility, and resistance to corrosion. Some of the most well-known precious metals include Gold, Silver, Platinum, Palladium, Rhodium, Iridium, Ruthenium, etc.,
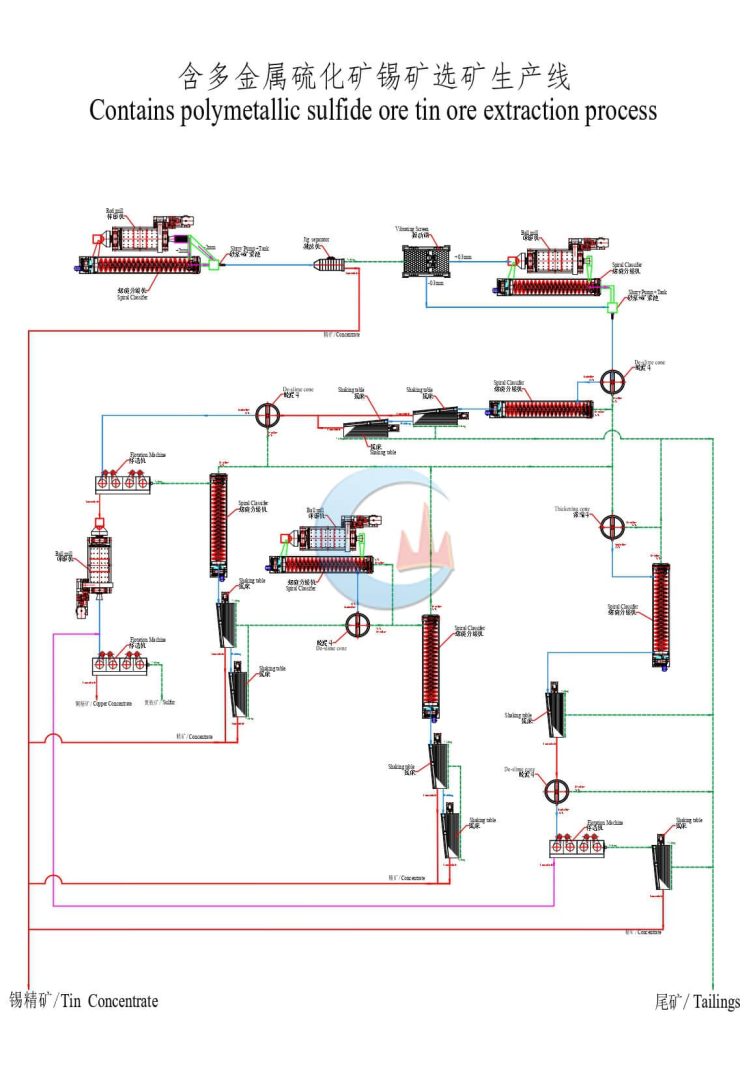
Non-ferrous Metals
Non-ferrous metals are metals that do not contain a significant amount of iron. These metals are valued for their various properties, including corrosion resistance, conductivity, and malleability. They are used in various applications, from construction and transportation to electronics and manufacturing. Non-ferrous metal ores are minerals or mineral combinations that contain these metals in varying concentrations. Here are some examples of non-ferrous metal ores: copper, aluminum ore(Bauxite), lead, zinc, tin, nickel, manganese, tungsten, rare earth elements ores, etc.
Ferrous Metals
Ferrous metals contain iron and are characterized by their magnetic properties, strength, and durability. These metals are widely used in various applications, including construction, manufacturing, and transportation. Ferrous metal ores are minerals or mineral combinations that contain iron in various forms. Here are some examples of ferrous metal ores: iron, magnetite, hematite, siderite, chromite, manganese, vanadium-titanium magnetite, taconite, etc.,
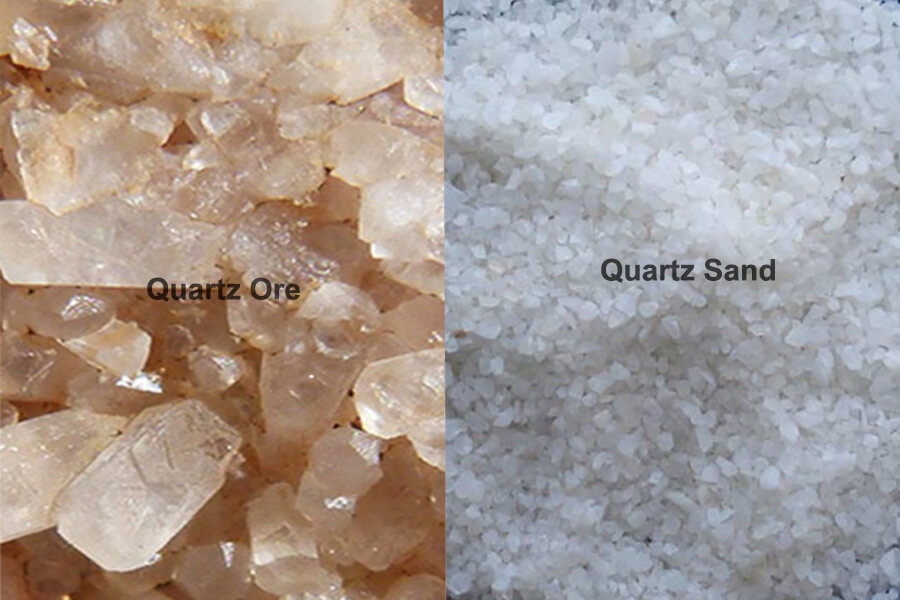
Non-Metals
Non-metals, unlike metals, do not exhibit metallic properties like electrical conductivity, malleability, and ductility. They include a wide range of elements and compounds, many of which are crucial in various industrial, chemical, and technological applications. While non-metals are not typically found in ore forms like metals, some non-metallic minerals are extracted for various purposes. Here are examples of non-metallic minerals that are often extracted: coal, salt (halite), gypsum, sulfur, phosphates, potash, quartz, clay, graphite, diamond, etc.,
New Energy Mineral
New energy minerals are a group of minerals and materials that have gained increasing importance in developing clean and renewable energy technologies. These minerals are essential components in various technologies that aim to reduce carbon emissions, increase energy efficiency, and transition from fossil fuels to cleaner energy sources. Some key new energy minerals include lithium, cobalt, graphite, rare earth elements (REEs), copper, silicon, vanadium, tellurium, cesium, gallium, indium, etc.,
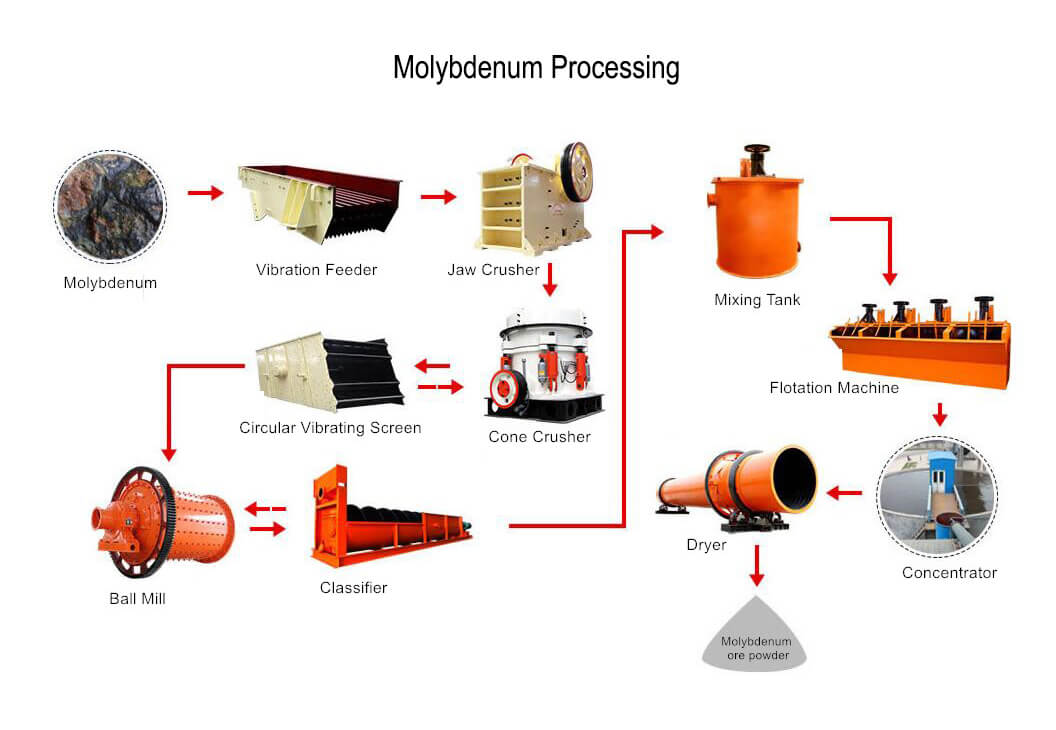
Rare Metal
Rare metals, also known as rare earth elements (REEs), are a group of 17 chemical elements in the periodic table, which include elements like lanthanum, cerium, neodymium, and yttrium. They are valuable due to their unique magnetic, luminescent, and catalytic properties, making them essential in various modern technologies, including electronics, renewable energy, and defense applications. Rare metal ores contain these elements, often in combination with other minerals. Here are some examples of rare metal ores: monazite, bastnäsite, xenotime, loparite, allanite, eudialyte, gadolinite, yttrium ores, etc.,
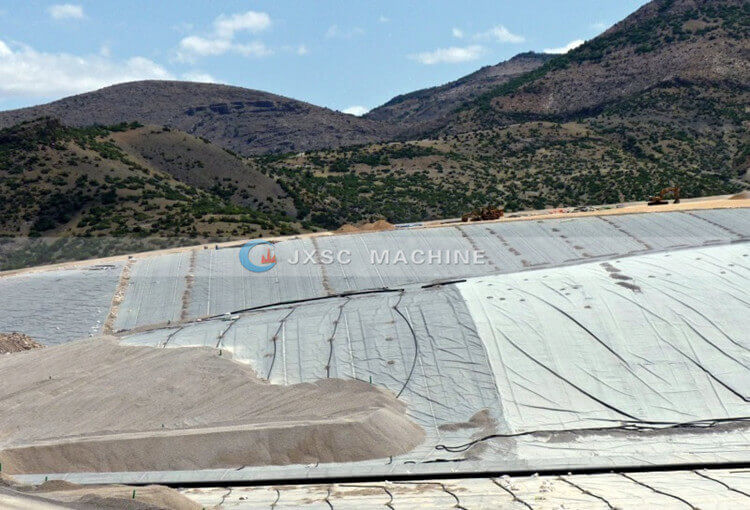
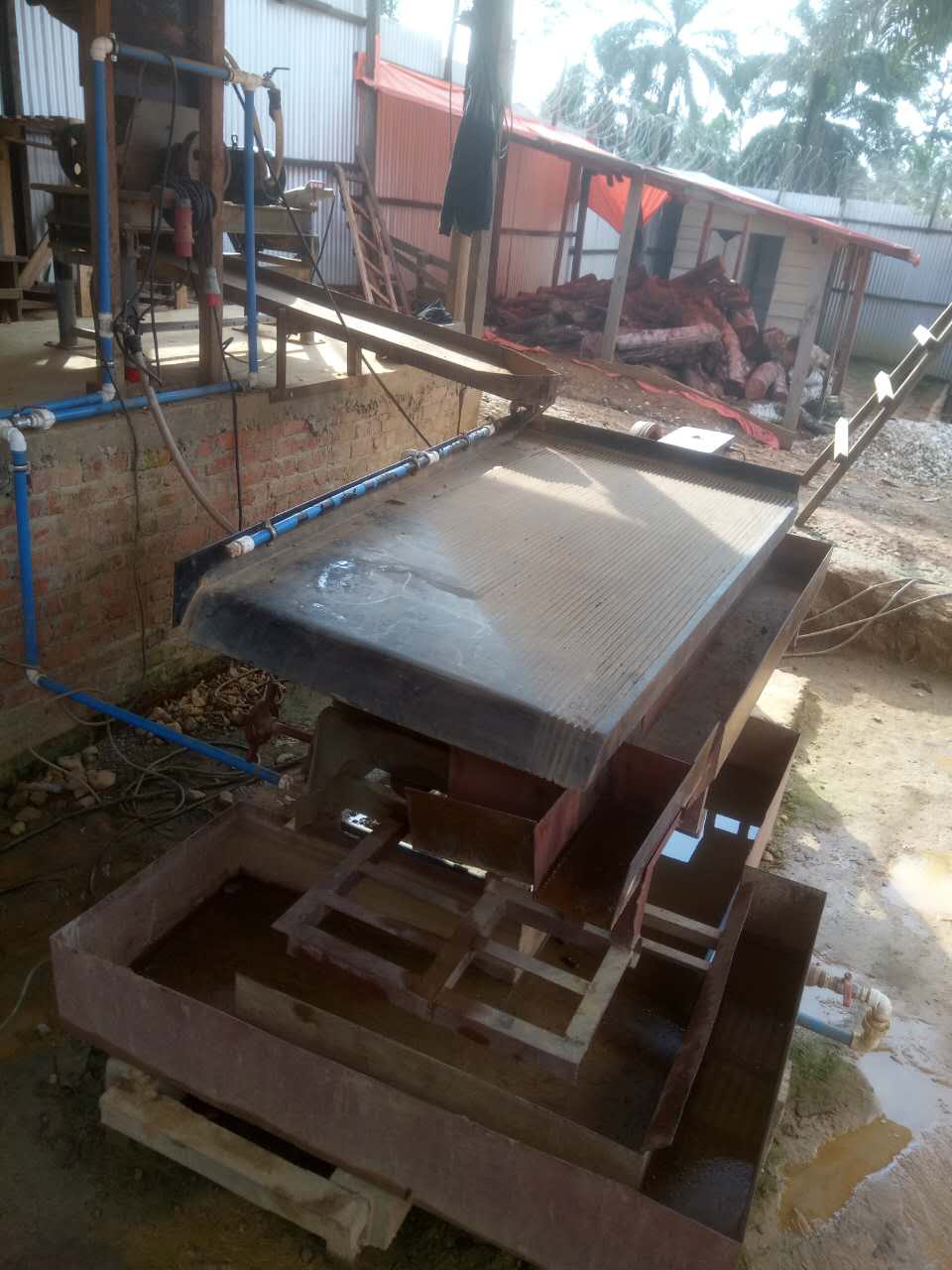
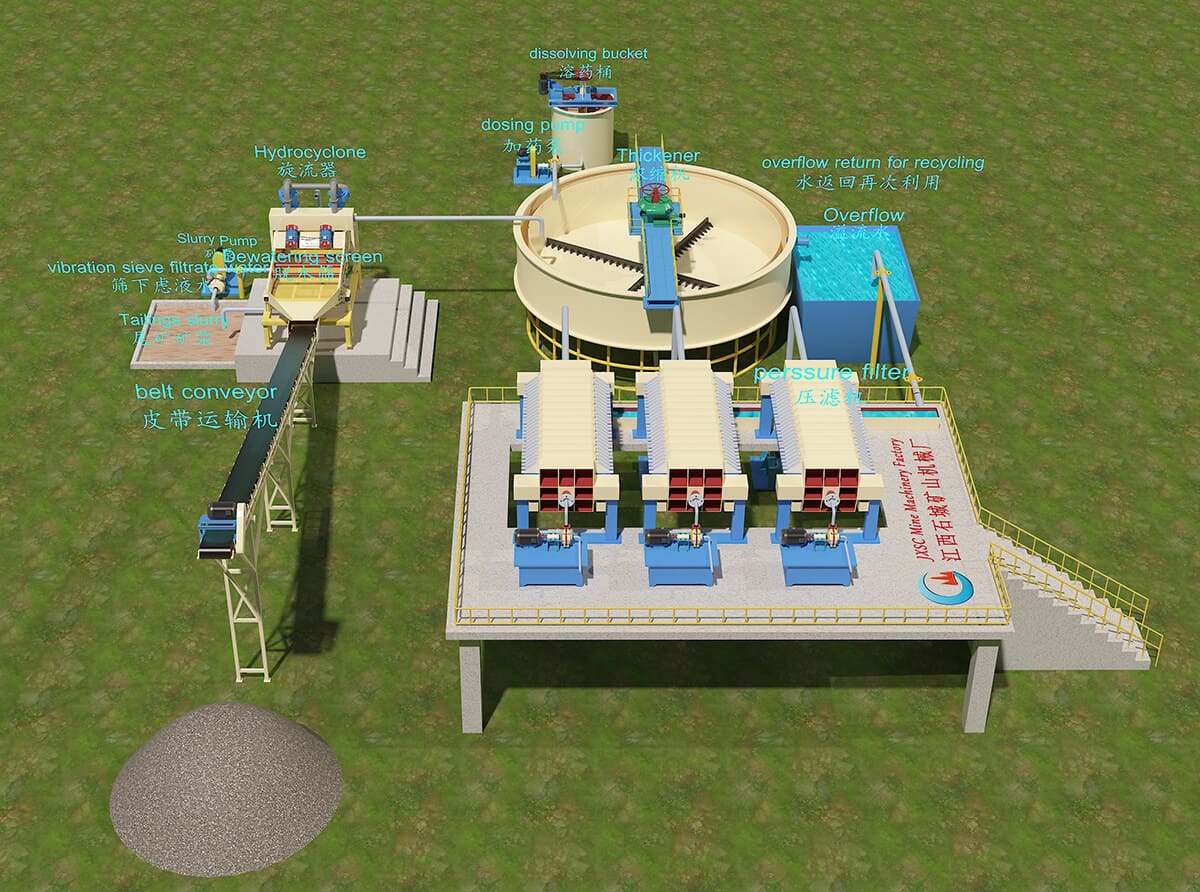
Tailings
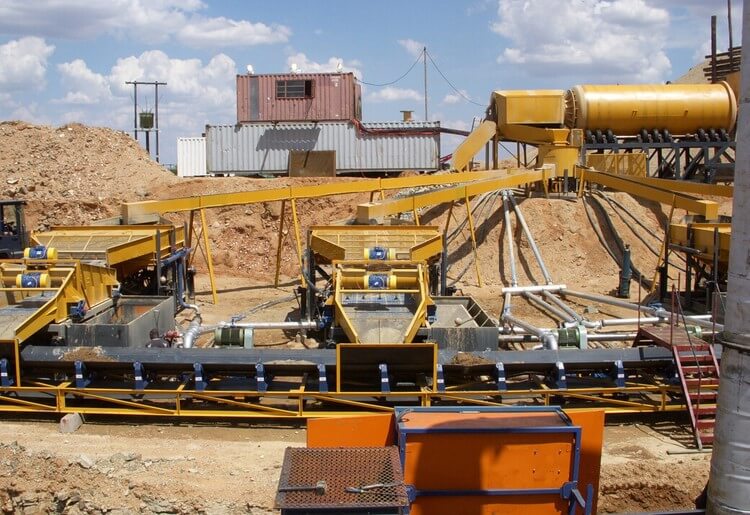
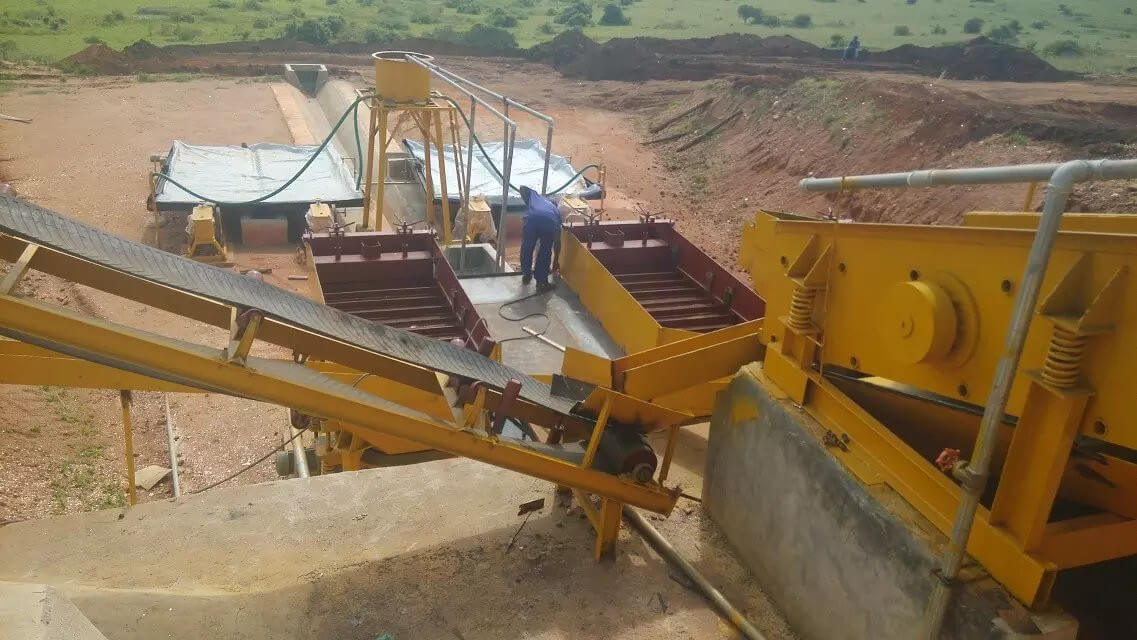
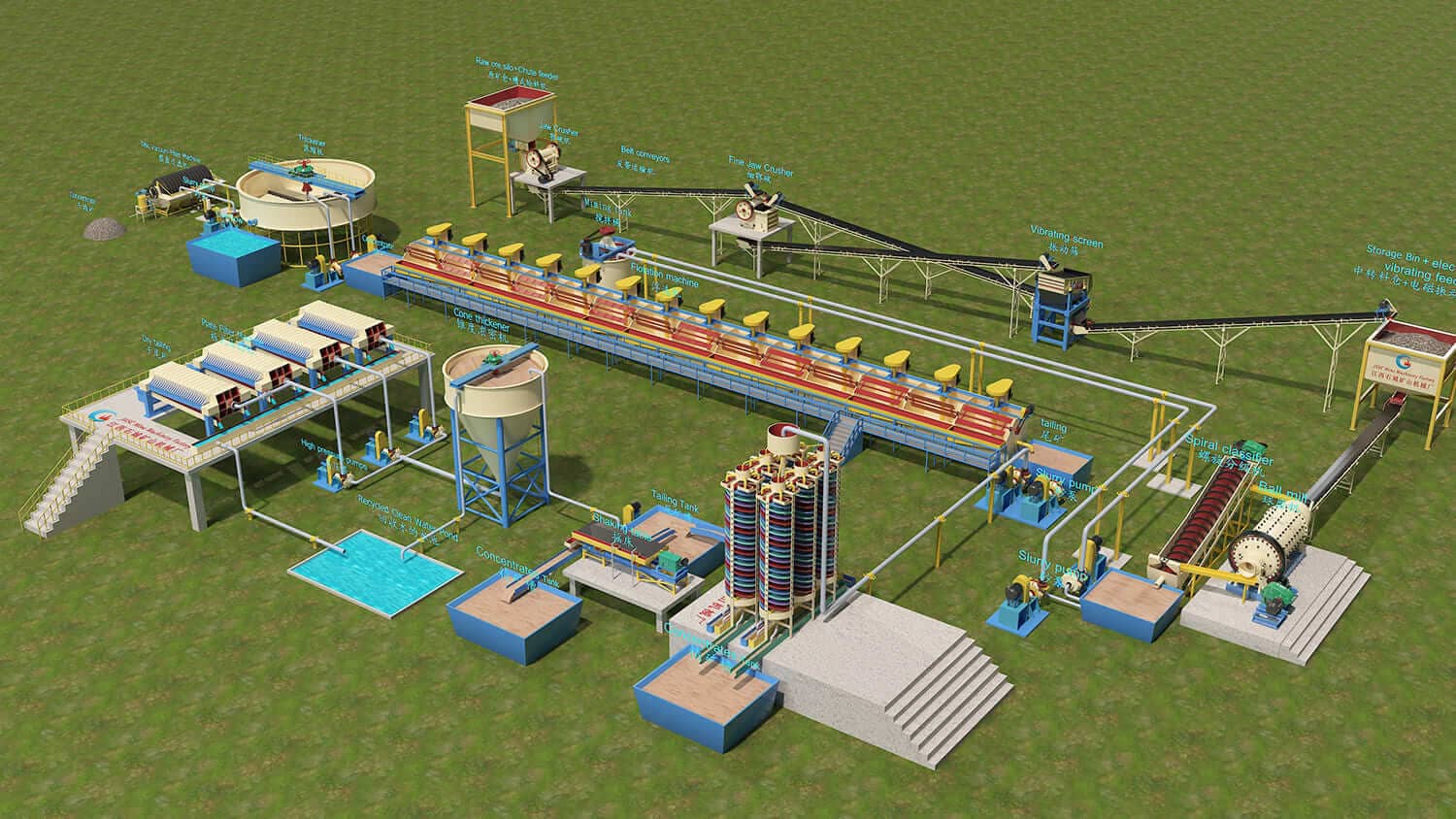
State-of-the-Art Mineral Processing Solutions
At JXSC Mineral, we are dedicated to transforming the mining and mineral processing extraction industry with our cutting-edge products and services. Our expertise and innovative solutions are designed to enhance efficiency, sustainability, and profitability for mining operations of all sizes. We are offering:
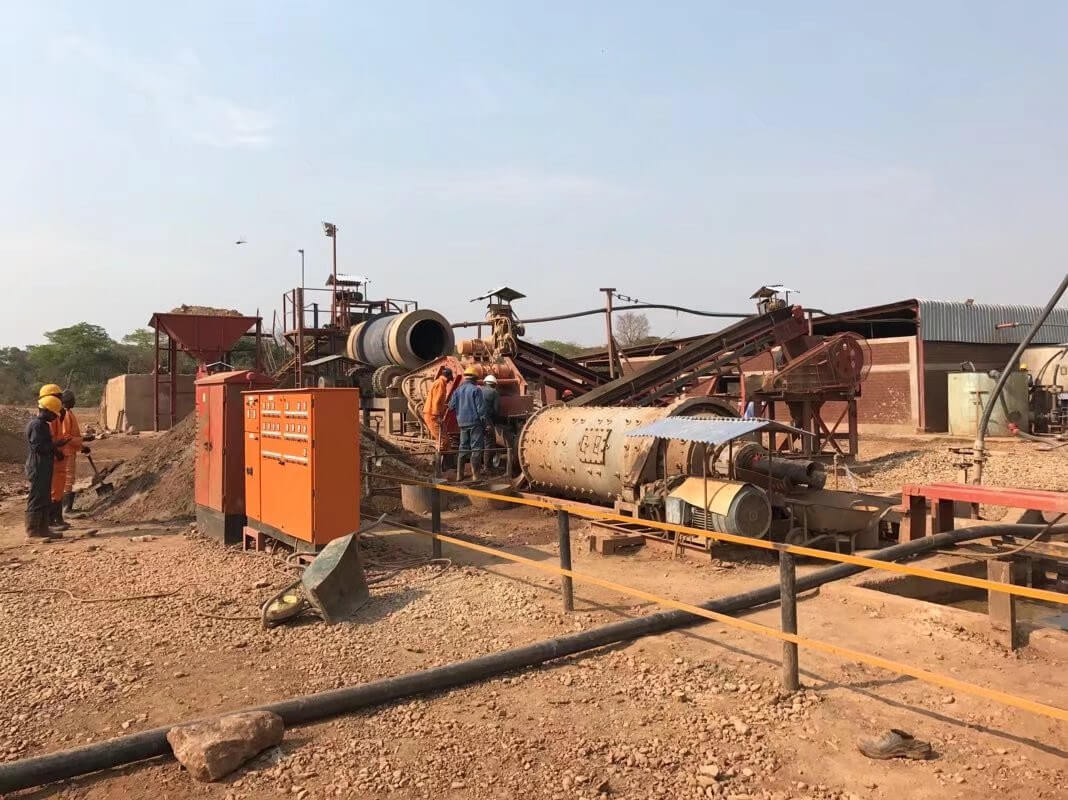
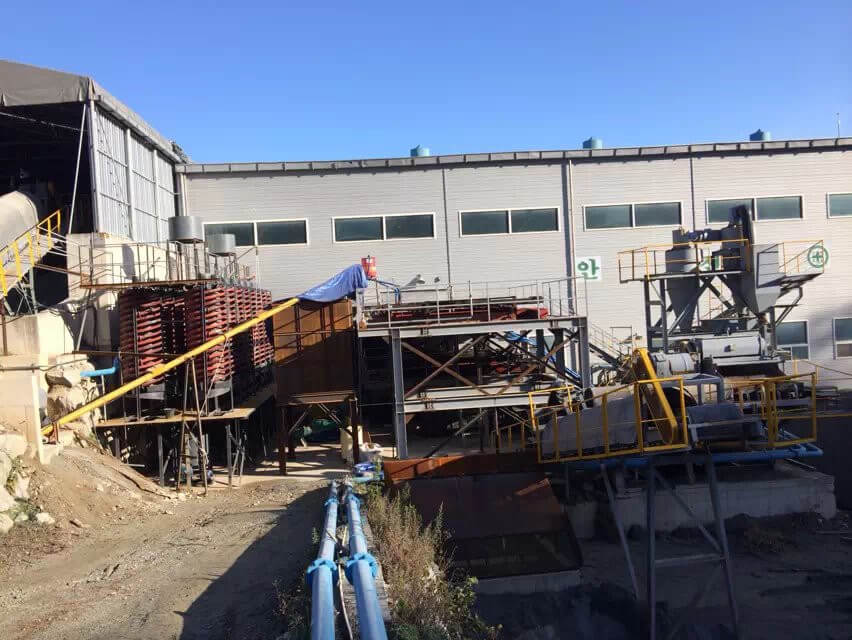
Advanced Mining Equipment
Conveyors
Robust systems for efficient material transportation.
Crushers and Grinders
High-performance equipment for reducing raw ore to manageable sizes.
Screening Machines
Advanced technology for separating valuable minerals from ore.
Flotation Cells
Efficient systems for extracting metals from ore.
Environmental Protection Equipment
- Dust Suppression Systems
Innovative solutions to minimize airborne dust. - Water Treatment Plants
Ensuring clean water discharge and reuse in mining operations. - Waste Management Systems
Effective waste handling to reduce environmental impact.
Comprehensive Services
Mining Consultancy
Feasibility studies, environmental impact assessments, and mine planning and design.
Plant Construction and Maintenance
Turnkey solutions for mining and processing plant construction, ongoing maintenance, and operator training.
Automation and Control Systems
Integrated control systems, remote monitoring, and data analytics for increased productivity and safety.
We deliver comprehensive solutions that drive efficiency, safety, and sustainability in the mining and mineral extraction industry. Our advanced equipment, state-of-the-art processing solutions, and expert services are designed to meet the diverse needs of modern mining operations.
Whether you want to enhance your current operations or embark on a new project, our team of professionals is here to support you every step. Contact us today to learn more about our innovative solutions and how we can help your mining and processing plant.