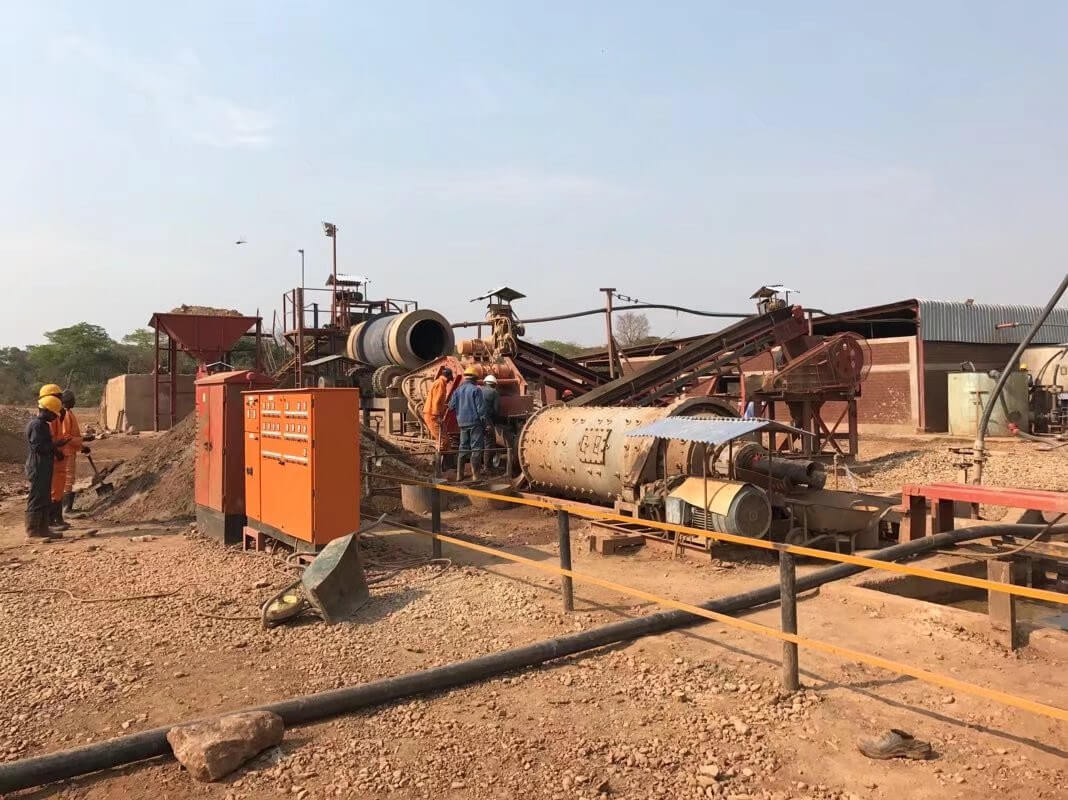
Beach Sand Separation
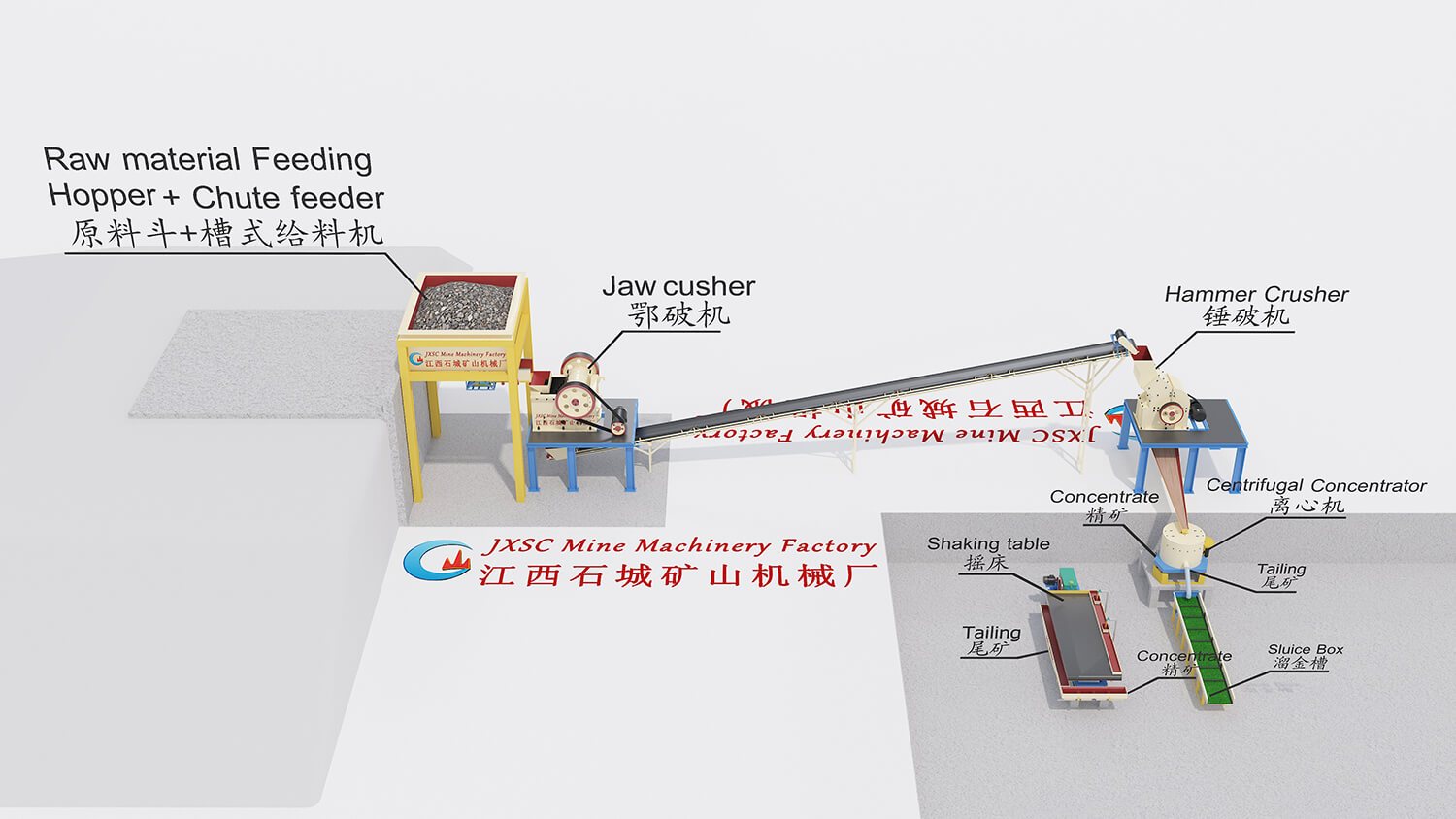
Beach sand mainly comprises rutile, tantalite, magnetite, xenotime, gold ore, iron ore, diamond, quartz sand, coal, and other minerals. The beach sand process is screening the impurities, following separating by gravity separation, magnetic separation, and drying. Finally, use magnetic separation + electric separation to select each required mineral.
Beach Sand Separation Process
Introduction
About Beach Sand
Beach sand refers to the secondary enrichment deposit formed by the accumulation of heavy mineral debris in the coastal zone due to the action of rivers, waves, tides, and ocean currents. It includes the placer deposits in the coastal area and the placer deposits formed on the seashore during the geological period and then below the sea surface due to the rise of the sea level or the decline of the coast. It mainly comprises rutile, tantalite, magnetite, xenotime, gold ore, iron ore, diamond, quartz sand, coal, and other minerals.
Beach sand has vast economic value. It has the advantages of wide distribution, exploration, mining, ore dressing, and convenient smelting. It has been valued by coastal countries and has become the world’s most crucial mining source of monazite, cassiterite, zircon, ilmenite, and rutile.
Mineral Processing
Beach Sand Concentration Separation
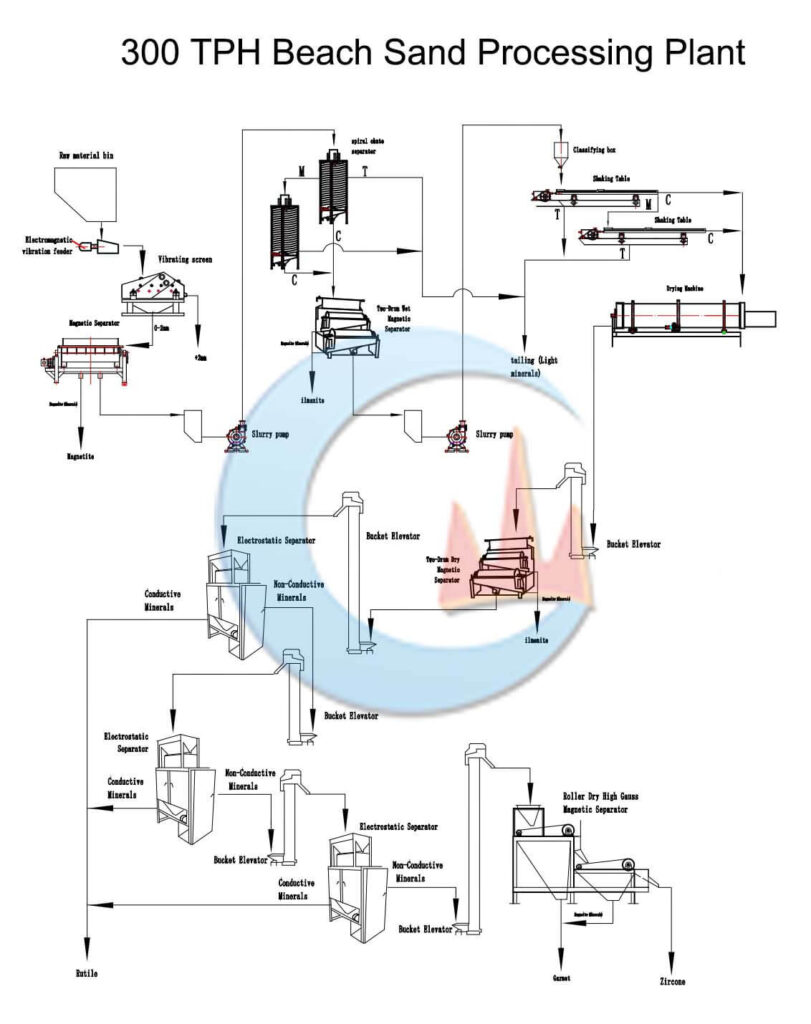
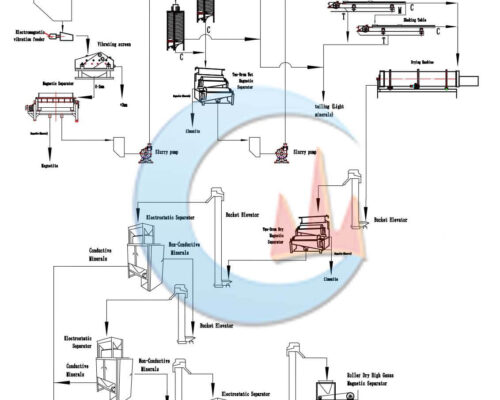
The common beneficiation process of beach sand is traditional gravity separation, dry magnetic separation, and electric separation combined.
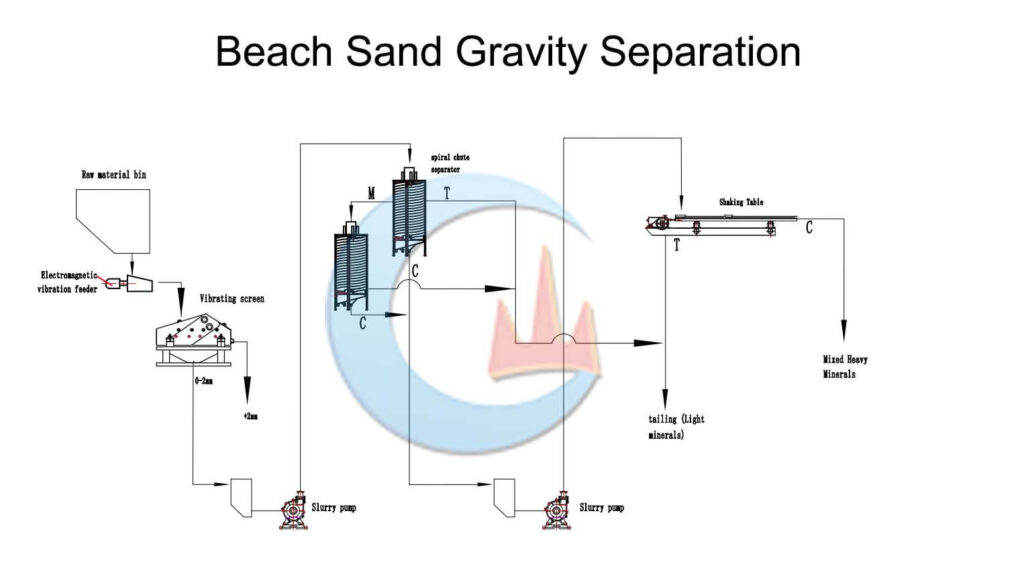
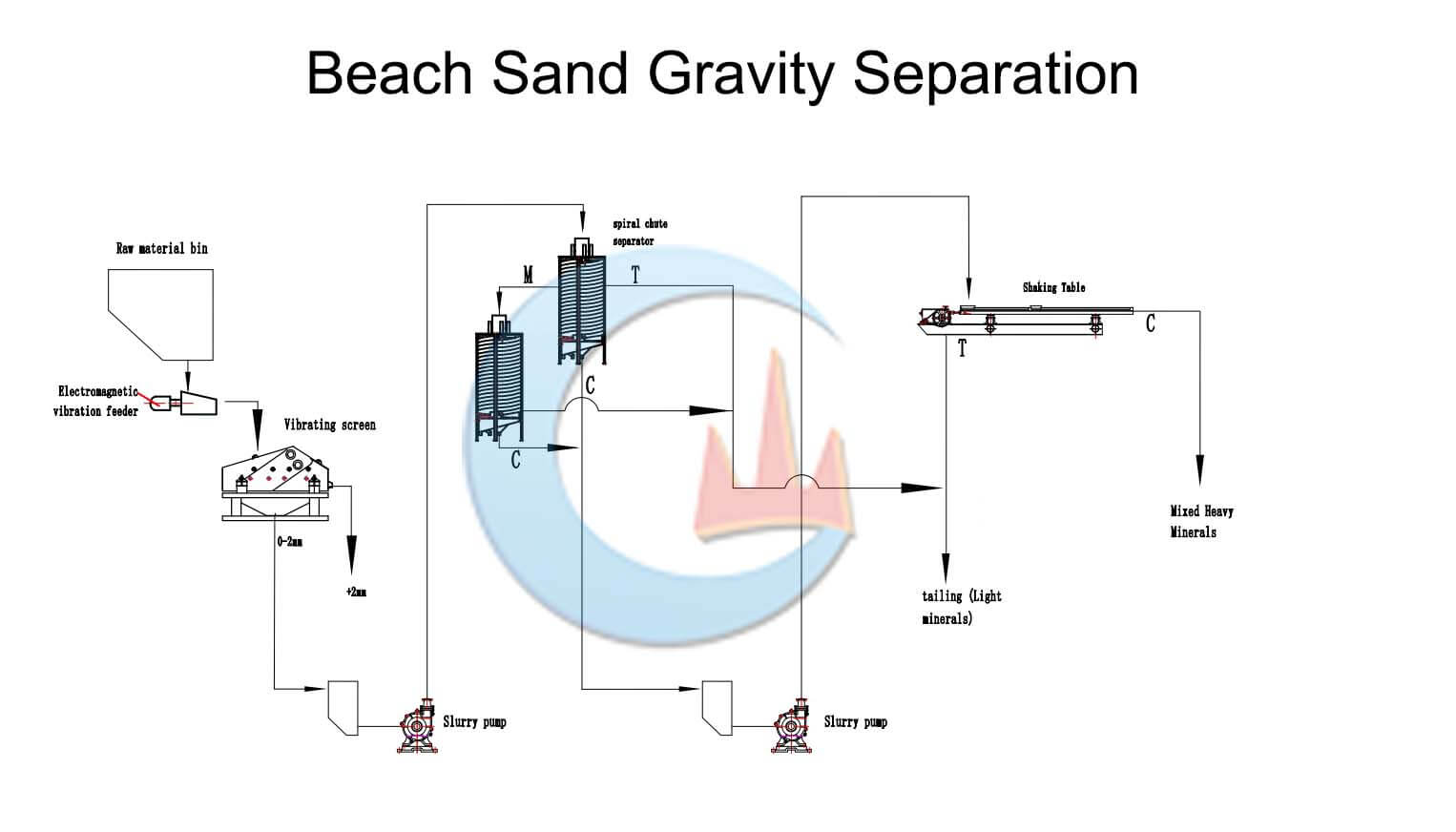
Beach Sand Gravity Separation
The gravity separation method uses the difference in density between rare earth minerals and gangue minerals for separation. Commonly used gravity separation equipment includes the spiral concentrator, shaker table, etc. Gravity separation is mainly used to separate rare earth minerals from gangue minerals, such as quartz and calcite with low density, to achieve pre-enrichment or obtain rare earth concentrate. Gravity separation is widely used in the production of beach sand.
Beach Sand Magnetic Separation
In beach sand(placer) beneficiation, weak magnetic separation often separates ilmenite from monazite, and strong magnetic separation separates monazite from zircon, quartz, and other minerals.
Beach Sand Electric Separation
Electric separation is a mineral processing method that uses the electrical difference between minerals to separate them in a high-voltage electric field. Electric separation has been widely used in separating rare metal minerals (such as zircon, ilmenite, monazite, and tantalum-niobium ore.)
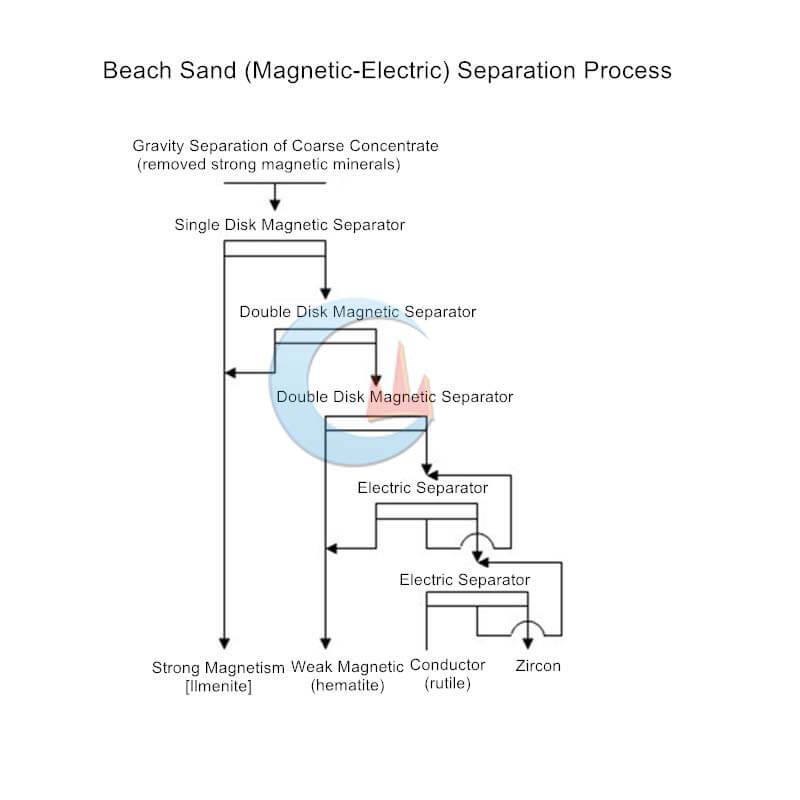
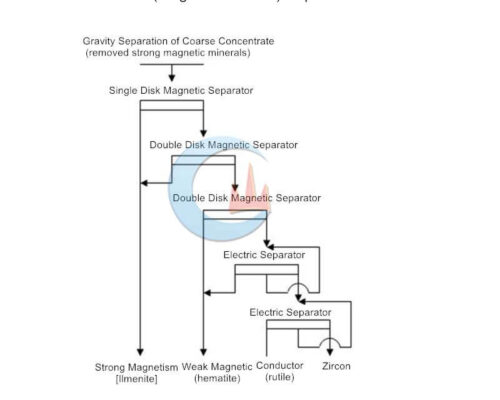
The main minerals recovered from the coarse concentrate of seashore placer are ilmenite, monazite, rutile, and zirconium fluorite. Ilmenite has the strongest magnetic properties among these minerals, followed by monazite. Rutile and zirconium Quartz is a non-magnetic mineral. However, the conductivity of rutile is much higher than that of zircon, so the combined process of magnetic separation and electric separation can be used.
Beach Sand Beneficiation Plant
Mineral Ores: The alluvial beach sand’s main metal minerals are zirconium fluorite, rutile, ilmenite magnetite, and hematite; the main gangue minerals are quartz, feldspar, and mica.
The mine adopts a strong magnetic-electric separation process because the magnetite has been removed during the gravity separation process, and the ilmenite has the strongest magnetism among the remaining minerals. The magnetic separation of magnetite is slightly weaker than that of ilmenite, and it is selected in a fine-sweeping double-disc magnetic separator. The magnetic field of the double-disk strong magnetic separator is higher than that of the single-disc magnetic separator. The rutile and zircon in the tailings are separated by one rough and one sweep electric separation. More zircons include body and other minerals, and it is often difficult to obtain suitable products and be discarded as tailings.