Rutile Processing & Beneficiation
Rutile ore is a complex ore composed of a variety of minerals. Its grade is low, and the particle size is tiny. The rutile concentrate requires a titanium dioxide content of more than 87.5%. Therefore, the rutile ore process often uses gravity separation, magnetic separation, flotation, and their combined process.
Rutile Beneficiation
Introduction
About Rutile
Rutile is the most common natural form of titanium dioxide. The chemical formula is TiO2, and the composition often contains Fe, Nb, Ta, Cr, Sn, and other elements. It belongs to the tetragonal crystal system; the crystals are columnar and needle-shaped. Rutile is an important raw material for producing chemical products such as titanium sponges and titanium dioxide. The colors are reddish-brown, purple, yellow, green, black, etc. Rutile can be formed in many rocks and can be seen in acidic magmatic rocks, pegmatites, crystalline rocks, gneiss, amphibolites, eclogites, etc. The coarse crystals are mainly produced in pegmatites. The rutile is transferred to the placer when the original rock is weathered.
Rutile Ore Types
- Regional sedimentary metamorphism
- Eclogite
- Hydrothermal alteration
- Metamorphic altered rock
- Weathering-sedimentary
Mineral Processing
Rutile Beneficiation Process
The rutile ore beneficiation process must adopt various beneficiation methods: such as a combined beneficiation process consisting of gravity separation, magnetic separation, flotation, electric separation, pickling, etc., to obtain high-quality rutile concentrate products.
1. Gravity Separation
Gravity separation is most suitable for processing placer rutile ore. In separating primary rutile ore, gravity separation is often essential for enrichment. In sorting rutile ore, gravity separation desliming and tailings are used as roughing operations, which can discard most of the slime. The shaking table can separate quartz, tourmaline, garnet, and part of white titanite as tailings. And the rutile is enriched in the shaking table’s medium ore and concentrate.
2. Magnetic Separation
Magnetic separation can separate magnetically conductive ilmenite, limonite, hematite, magnetite, and other magnetic minerals from non-magnetically conductive rutile minerals. In production practice, we can see that a small amount of rutile enters the magnetic product, and the color of this rutile is black. After analysis, this rutile contains more than 2% iron oxide and has weak magnetic properties. This kind of rutile is usually called iron rutile. In the separation of rutile ore, magnetic separation can be effectively used for pre-selection and concentration of rutile ore if combined with other beneficiation methods.
3. Electric Selection
Electric beneficiation is a mineral processing method based on the conductivity of minerals and sorting according to the different conductivity of the surface of various minerals. Since silicate, zircon, and white titanium are non-conductive, electro-separation can easily realize the effective separation of conductive and non-conductive minerals, further improving the grade of rutile concentrate and reducing the content of impurities.
4. Flotation
Flotation is an effective method for separating fine-grained rutile and reducing metal loss.
5. Pickling
After the rutile ore is separated by gravity separation, magnetic separation, electric separation, and flotation, many impurity minerals such as silicate, carbonate, and iron still adhere to the edges and cracks of the rutile. The pickling process can remove these impurities and improve the quality of the concentrate.
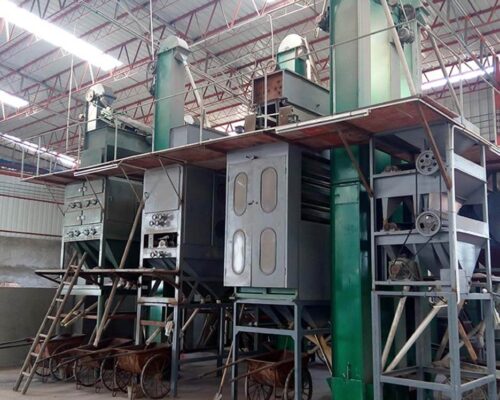
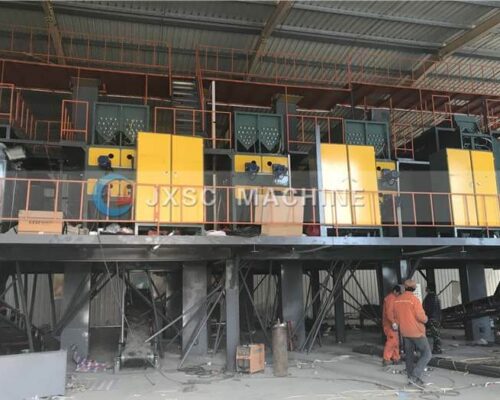
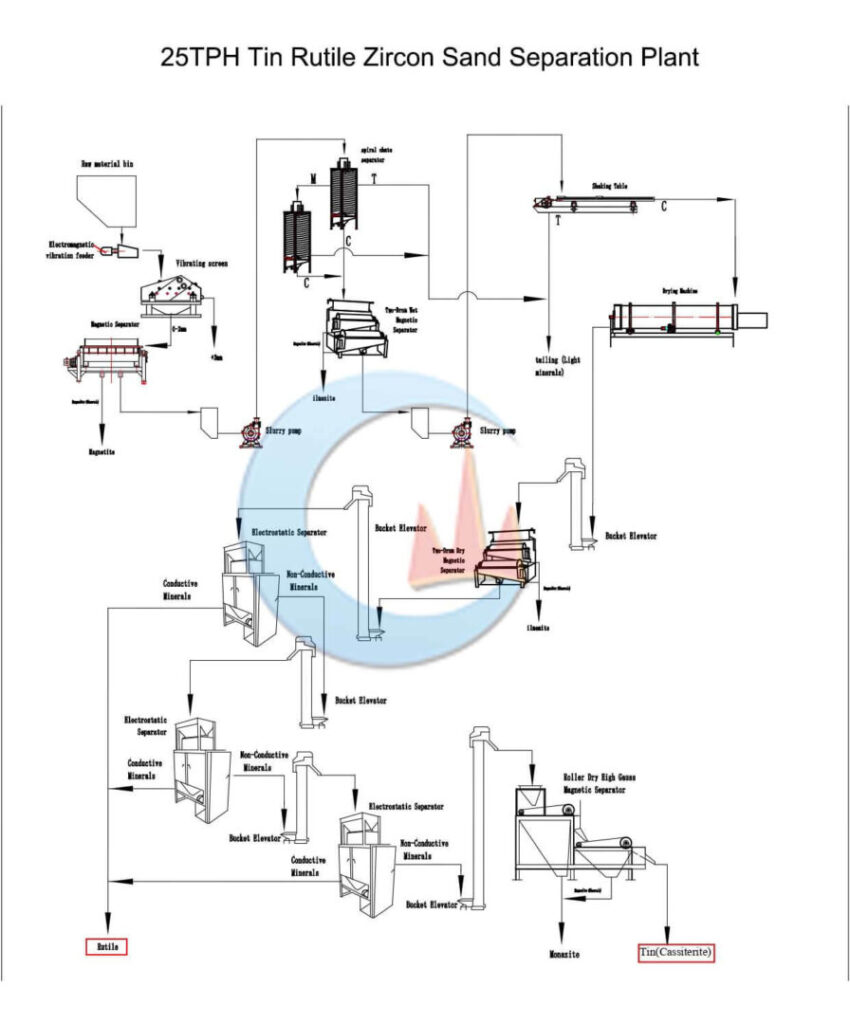
Rutile Sand Processing Plant
Mineral Ore Introduction
- Capacity: 100tph
- Above 2mm impurities are removed
- Need separate rutile, monazite, zircon, ilmenite, magnetite from the beach sand.
Processing Plant Explanation
- The excavator or Loader feeds raw sand to the raw ore bin, then feeds the vibrating screen through the electromagnetic vibrating feeder.
- Vibrating screen with one layer screen with 2mm mesh size to remove above 2mm impurities.
- Below 2mm go to magnetic separator by slurry pump for separating out magnetite.
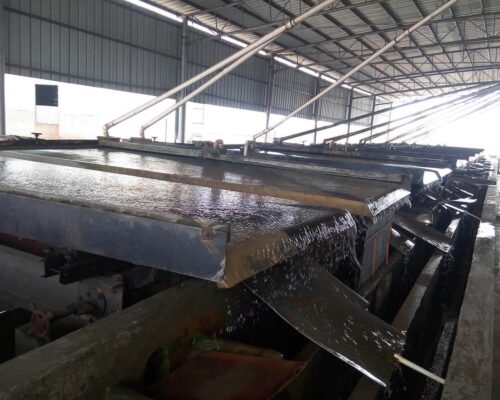
- The output of the magnetic separator is sent to the spiral chute by a slurry pump. Through gravity separation method to remove light minerals.
- The spiral chute gravity separation plant has two stages: the middling from the first stage spiral chute plant goes to the second stage spiral chute for reprocessing.
- All concentrates from two stages of spiral chute plants are sent to 1st double drum magnetic separator for separating out ilmenite.
- The output of 1st double drum magnetic separator is sent to the shaking table by a slurry pump for removing light minerals by gravity principle.
- The Shaking table has two stages: the middling from the first stage shaking table is sent to the second stage shaking table for further processing by a slurry pump.
- All concentrate from the two stages of the shaking table plant is sent to the rotary dryer for drying material.
- After drying, dry materials through the hoist machine to the 2nd double drum magnetic separator to separate the ilmenite.
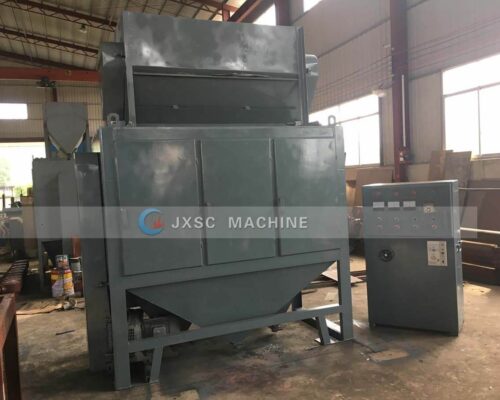
- Other minerals from 2nd double drum magnetic separator go to 1st electrostatic separator through the hoist machine for separating out rutile, other minerals through the hoist machine to 2nd electrostatic separator for separating out rutile, other minerals through the hoist machine to 3rd electrostatic separator for separating out rutile.
- Other minerals from the 3rd electrostatic separator go to the double roller strong magnetic separator via a hoisting machine for separating out zircon and monazite.